News
Delta flight dl275 diverted lax: What Happened and Why It Matters

Imagine being thousands of feet in the air, halfway across the vast Pacific Ocean, on your way to an exciting destination like Tokyo. Suddenly, the calm hum of the engines changes, and the captain’s voice comes over the intercom, announcing an unexpected change of plans: your flight is diverting. This was the reality for passengers on Delta Flight DL275, a routine service from Detroit to Tokyo Haneda, when it made an unscheduled landing at Los Angeles International Airport (LAX). This incident, which occurred recently on May 26, 2025, sparked immediate questions about the flight, its passengers, and the complex safety protocols that govern international air travel.
The Journey Interrupted: A Closer Look at DL275’s Diversion
Delta Air Lines flight DL275 is a daily, long-haul service connecting Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW) with Tokyo Haneda Airport (HND) in Japan. On this particular day, May 26, 2025, the flight was operated by an Airbus A350-900, a modern wide-body aircraft known for its efficiency and comfort on long routes. The specific aircraft involved bore the registration N508DN, a twin-jet that is approximately seven years old and part of Delta’s extensive A350 fleet.
The journey began with a slight delay, as the inbound flight (DL133 from Amsterdam Schiphol Airport) arrived late, pushing DL275’s departure time back by almost two hours. Eventually, the Airbus A350-900 lifted off from Detroit at 3:53 PM local time. For hours, the flight proceeded as planned, cruising over the North American continent and into the vast expanse of the Pacific. However, as the aircraft approached the Bering Sea, a critical issue arose.
Reports indicate that one of the aircraft’s Rolls-Royce Trent XWB engines experienced a problem with its anti-ice system. This system is crucial, especially when flying at high altitudes where temperatures can drop significantly below freezing, making ice formation on engine components a serious risk. While the exact nature and severity of the malfunction were not immediately disclosed, the flight crew, prioritizing the safety of everyone on board, made the decision to divert. Instead of continuing west towards Tokyo, the aircraft made a significant turn and headed southeast, setting a new course for Los Angeles International Airport (LAX).
The diversion added a considerable amount of flight time to the journey. The flight, which was initially scheduled for approximately 13 hours and 10 minutes to Tokyo, ended up flying for more than 12 hours and 15 minutes just to reach LAX. This meant that by the time it touched down on runway 06R at LAX in the middle of the night (01:08 AM local time on May 27, 2025), passengers had been in the air for almost as long as the entire planned trip to Tokyo. The decision to divert to LAX, despite other closer Delta hubs like Seattle, was likely a strategic one, given LAX’s status as a major Delta hub with the necessary facilities, maintenance capabilities, and support staff to handle such an unexpected arrival.

Why Diversions Happen: Understanding Aviation Safety
Flight diversions, while disruptive, are a testament to the robust safety systems and highly trained professionals within the aviation industry. They are not uncommon, and they happen for a variety of reasons, all primarily centered around ensuring the safety of passengers and crew. In the case of Delta DL275, the reported issue with the engine’s anti-ice system falls under the category of a mechanical or technical malfunction.
Here are some of the most common reasons why flights are diverted:
- Technical or Mechanical Issues: Like the anti-ice system problem on DL275, aircraft can experience a wide range of technical faults during flight. These can include issues with engines, hydraulic systems, electrical systems, pressurization, or any other critical component that might compromise the aircraft’s airworthiness or the safety of its operation. Pilots and airlines always err on the side of caution when these issues arise.
- Medical Emergencies: A passenger or crew member experiencing a severe medical emergency onboard often necessitates a diversion. Getting the individual immediate medical attention is paramount, and diverting to the nearest suitable airport with medical facilities is often the quickest way to achieve this.
- Unruly Passengers: While less common than technical or medical reasons, a passenger whose behavior poses a threat to the safety or comfort of others, or who is disruptive to the flight operations, can lead to a diversion. Airlines and law enforcement take such incidents very seriously.
- Weather Conditions: Adverse weather at the destination airport (e.g., severe storms, heavy fog, high winds) can make landing unsafe. In such cases, flights are diverted to alternate airports where weather conditions permit a safe landing.
- Air Traffic Control (ATC) Restrictions or Airport Closures: Sometimes, unexpected events like an airport closure due to an incident, runway issues, or even a sudden increase in air traffic can lead to ATC directing a flight to an alternate airport.

- Fuel Considerations: While pilots plan for sufficient fuel for the primary route and alternate airports, unforeseen circumstances like extended holding patterns due to air traffic or unexpected weather can deplete fuel reserves, necessitating a diversion to the nearest suitable airport.
In all these scenarios, the decision to divert is made by the flight crew, often in consultation with airline operations centers and air traffic control. Their primary goal is always to land the aircraft safely, and they are trained to assess the situation and choose the best course of action, which includes selecting an appropriate alternate airport that can handle the aircraft type and provide the necessary support. For a large aircraft like the A350-900, this typically means diverting to a major international airport with extensive facilities and Delta’s own operational presence.
The Passenger Experience: Dealing with the Unexpected
For the nearly 300 passengers on board Delta DL275, the diversion to LAX undoubtedly turned a planned international journey into a long and uncertain ordeal. Being diverted, especially on a trans-Pacific flight, can be a frustrating and anxiety-inducing experience. Passengers often face:
- Extended Travel Time: As seen with DL275, the diversion itself added many hours to the travel time, effectively doubling the length of the initial flight segment.
- Uncertainty and Delays: Once on the ground at the diversion airport, passengers often face delays as the airline works to assess the situation, arrange for a new aircraft, re-crew the flight, or make alternative travel arrangements. This can involve waiting for hours in the terminal, or even having to spend the night.
- Logistical Challenges: Depending on the reason for the diversion and the facilities at the alternate airport, passengers might encounter challenges with immigration and customs (especially for international flights diverted to a different country than their destination), baggage handling, and access to food and accommodations.
- Impact on Connecting Flights: For passengers with connecting flights, a diversion almost certainly means missing their onward connections, leading to further rebooking and delays.
- Discomfort and Fatigue: Long hours in an airplane, followed by an unexpected landing and subsequent waiting, can lead to significant discomfort and fatigue for travelers.
Airlines generally have established protocols for handling diverted passengers. This typically includes:
- Providing Information: Keeping passengers informed about the reason for the diversion, the expected duration of the delay, and the plans for onward travel is crucial. Clear and frequent communication helps manage expectations and reduce anxiety.
- Basic Amenities: For extended delays, airlines are usually responsible for providing food and beverages. If an overnight stay is required, they often arrange for hotel accommodations and ground transportation.
- Rebooking and Re-routing: The airline will work to rebook passengers on the next available flight to their original destination, either on their own airline or on partner airlines. In some cases, a replacement aircraft may be flown to the diversion airport to continue the journey.
- Compensation: While not always legally required for all types of diversions (e.g., weather-related), airlines may offer compensation in the form of travel vouchers, miles, or refunds, especially if the diversion was due to an issue within the airline’s control, such as a mechanical problem.
Delta Air Lines, as a major carrier, would have initiated these procedures to assist the passengers of DL275. Their goal would have been to get passengers to Tokyo as quickly and comfortably as possible, while prioritizing safety above all else.
The Bigger Picture: Air Traffic Control and Airline Response
The successful diversion of Delta DL275 to LAX highlights the intricate coordination between the flight crew, the airline’s operations center, and air traffic control (ATC). When a pilot declares an emergency or requests a diversion, ATC plays a crucial role in:
- Clearing Airspace: ATC works to clear the necessary airspace for the diverting aircraft, ensuring a safe and clear path to the alternate airport.
- Providing Guidance: Controllers provide vectors, altitude clearances, and other crucial information to guide the aircraft safely to its new destination.
- Coordinating with Airport Services: ATC alerts the ground services at the diversion airport, including emergency services (fire, medical), ground handling crews, and airline personnel, so they are prepared for the aircraft’s arrival.
Airlines, on their part, activate their operational control centers (OCCs) during such events. These centers are staffed by experts who monitor flights worldwide, manage unexpected events, and make critical decisions regarding diversions, re-routing, and passenger support. Their role includes:
- Technical Support: Engineers and maintenance specialists assess the reported issue and advise the flight crew.
- Logistics and Planning: Teams work to find alternative aircraft, secure new crew members if needed (due to duty time limits), and arrange for passenger rebooking and accommodations.
- Communication: Communicating with passengers, ground staff, and regulatory authorities.
The prompt and safe landing of DL275 at LAX demonstrates the effectiveness of these interconnected systems and the professionalism of everyone involved, from the pilots in the cockpit to the air traffic controllers on the ground.
Learning from Diversions: Enhancing Future Travel
Every flight diversion, especially one involving a significant technical issue like the engine anti-ice system on DL275, serves as a valuable learning opportunity for airlines and aviation authorities. Investigations, such as those that would follow this incident, aim to:
- Identify the Root Cause: Determine precisely why the anti-ice system malfunctioned.
- Prevent Future Occurrences: Implement corrective actions, which could include revised maintenance procedures, software updates, or even modifications to aircraft components.
- Improve Operational Responses: Refine existing protocols for handling similar situations in the future, from crew training to passenger communication.
For passengers, understanding the reasons behind diversions and the procedures airlines follow can help manage expectations and reduce stress during such unexpected events. While no one wishes for a flight diversion, knowing that these measures are in place to prioritize safety can offer some reassurance.
In conclusion, the diversion of Delta Flight DL275 to LAX was an unexpected detour for nearly 300 travelers. Caused by a technical issue with an engine’s anti-ice system, it highlighted the constant vigilance required in modern aviation. More importantly, it underscored the dedication of flight crews, the sophistication of air traffic control, and the comprehensive operational responses by airlines, all working in harmony to ensure that even when plans go awry, the safety and well-being of those in the sky remain the absolute top priority. This incident, while disruptive, ultimately reinforces the incredible safety record of air travel and the continuous efforts to make every flight as secure as possible.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a flight diversion? A flight diversion happens when a plane has to change its planned route and land at an airport other than its original destination. This is usually due to unexpected events that make continuing to the original destination unsafe or impossible.
- Why did Delta Flight DL275 divert to LAX? Delta Flight DL275 diverted to LAX because of a problem with the anti-ice system on one of its Rolls-Royce Trent XWB engines. This system is very important for preventing ice from building up on the engine, especially at high altitudes.
- When did this diversion happen? The diversion of Delta Flight DL275 to LAX happened on May 26, 2025, with the aircraft landing in Los Angeles on May 27, 2025.
- What kind of plane was involved in the diversion? The aircraft involved was a modern Airbus A350-900, which is a wide-body, twin-engine jetliner often used for long-haul international flights. The specific plane had the registration N508DN.
- How long did the flight last before it landed in LAX? The flight from Detroit to Los Angeles, after the diversion, took about 12 hours and 15 minutes. This was almost as long as the entire scheduled flight to Tokyo.
- What happens to passengers when a flight is diverted? When a flight is diverted, airlines work to take care of the passengers. This often includes giving them updates, providing food and drinks, arranging hotel stays if needed, and rebooking them on other flights to their final destination.
- Is it common for flights to be diverted for mechanical issues? While not an everyday occurrence, flight diversions due to mechanical issues do happen. They are a sign that the airline and flight crew are prioritizing safety and taking immediate action when a problem arises with the aircraft.
- Why was LAX chosen as the diversion airport instead of somewhere closer? LAX was likely chosen because it is a major Delta Air Lines hub. This means it has the necessary facilities, maintenance teams, spare parts, and support staff to handle a large aircraft like the A350-900 and assist its passengers effectively.
- Who makes the decision to divert a flight? The final decision to divert a flight is made by the flight crew, specifically the captain. They work closely with the airline’s operations center and air traffic control to decide the best course of action for safety.
- What is the significance of this diversion for aviation safety? This diversion, like all others, shows how important strict safety protocols are in aviation. It also highlights the quick thinking and expertise of flight crews and ground support teams who work together to manage unexpected situations and ensure everyone on board lands safely. Each incident provides valuable lessons that help further improve airline operations and aircraft design.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
What Is imamia student organization? A Simple Guide for Everyone

Imamia Students Organization (ISO) is a Shia Muslim students group in Pakistan. It works with young people, mostly students, and helps them in study, faith, and social life. ISO is active in many schools, colleges, and universities across the country.
In this article, we will look at ISO in simple and clear words. You will learn about its history, goals, work, and also some common questions people ask about it.
1. Short History of Imamia Students Organization
ISO started on 22 May 1972 at the University of Engineering and Technology UET Lahore. A group of scholars and students felt that Shia youth needed a platform in colleges and universities. They wanted a group that could guide students in faith and help them face modern challenges.
Some important early figures include scholars like Ayatollah Syed Murtaza Hussain Sadar ul Fazil, Molana Agha Ali Moosvi, Molana Safdar Hussain Najafi, and Dr. Muhammad Ali Naqvi. They helped shape the first plan and structure of the organization.
From a small beginning in one university, ISO grew step by step. Now it has units in many regions of Pakistan, including big cities and smaller towns. Reports say it works in all provinces and also in areas like Azad Kashmir and Gilgit Baltistan.
2. Main Aims and Ideas of ISO
ISO is a student based and faith based organization. It focuses on Shia students but often joins wider Muslim and social causes. Its main aims are:
Promote Islamic values
ISO wants students to learn the teachings of the Qur’an and the Ahl al Bayt family of the Prophet. It tries to make faith part of daily life, not only rituals.
Build strong belief and identity
ISO works to strengthen the religious beliefs aqaid and ideas of the youth. It wants young people to feel confident as Muslims and as Shias in modern society.
Support education
Many students in Pakistan face money problems. ISO tries to support such students with guidance, book banks, and sometimes financial help.
Encourage unity and peace
The organization talks about unity among Muslims and respect for others. Public statements from ISO say that it is not a hate group and that it stands against injustice and sectarian violence.
In simple words, ISO wants students to be good Muslims, good citizens, and good learners.
3. How ISO Is Organized
ISO has a structured system so it can work in many places at the same time.
Units
The basic level is the unit. A unit works in one school, college, university, or local area. Active members in that area plan small events, classes, or study circles.
Divisions or Regions
Several units together form a division or region. For example, ISO Karachi Region looks after many city units in Karachi.
Central level
On the top, there is a central structure with office holders like a Secretary General and other leaders. The head office is at Al Mustafa House, Lahore.
Membership is usually open to Shia students in high schools, colleges, and universities. There are rules of discipline, regular meetings, and training for members.

4. Main Activities and Programs
ISO is known for a wide range of activities. These can be grouped into a few simple parts.
4.1 Religious and spiritual programs
ISO holds many religious programs during the year
- Majalis and gatherings in Muharram and Safar
- Programs on events like Milad un Nabi, Eid e Ghadir, and other important dates
- Quran study circles and sessions about Hadith and Islamic history
These programs try to connect young people with their faith in a calm and clear way.
4.2 Education and literacy work
ISO strongly focuses on education. In some places it has projects like Body of Literacy Development BOLD and other study programs to help students
- Tuition or study classes for school exams
- Book banks and distribution of used books
- Career guidance for choosing subjects and universities
- Help for competitive exams
Such projects are important for students from low income families who cannot pay for private coaching.
4.3 Social welfare and charity
ISO and its volunteers also join many social welfare activities
- Blood donation drives especially in Muharram. These drives help many thalassemia patients and others in need
- Relief work in times of floods, earthquakes, or violence in some regions
- Medical camps and support for poor families
- Food and ration distribution in Ramadan and other times
These efforts give students a chance to serve society and to learn empathy.
4.4 Student rights and campus issues
Like many student groups in Pakistan, ISO sometimes speaks about student rights
- Demand for better facilities in universities
- Talks and conferences about the restoration of student unions
- Seminars on education policy and social issues
These activities link religious and social awareness with real problems that students face every day.
5. Role of ISO in Student Life
For many Shia students, joining ISO is not only about politics or activism. It is also about belonging.
Community and friendship
ISO units give a space where students can meet others who share similar beliefs. They make friends, discuss problems, and feel less alone on campus.
Training and leadership
Active members often learn how to plan events, speak in public, manage teams, and solve conflicts. These are useful skills for later life as well.
Moral and personal growth
Regular programs, camps, and study circles try to build good character such as honesty, service, patience, and respect for others.
Student life is never perfect. But for many youth, ISO becomes an important part of their identity and learning.
6. Criticism and Challenges
Like many student organizations, ISO also faces some criticism and problems.
Clashes with other groups
At some points in history, there have been clashes on campuses between ISO and other student organizations. Some of these events turned violent and were reported in the media.
Claims about foreign funding
Some writers and critics have claimed that ISO receives financial support from outside Pakistan. ISO leaders have replied that the group is self funded by members and only takes moral or spiritual guidance from outside scholars, not money.
Security and sectarian tension
In some areas, Shia groups including ISO members have faced security risks because of sectarian violence. This makes their work harder and sometimes dangerous.
It is important to see these points in context. Student politics in Pakistan has a long and complex history. Many different groups not only ISO have faced both praise and criticism.
7. Why ISO Matters Today
Even after more than 50 years, ISO is still active in Pakistan.
It matters because
- It supports young people in a time of fast change and confusion
- It keeps many students connected with their faith in a thoughtful way
- It runs real projects that help with education, health, and social welfare
- It gives Shia students a voice in campuses where they might feel weak or alone
Some people agree with ISO on everything, some do not. But it is clear that the organization plays a strong role in the lives of many students across Pakistan.
8. Frequently Asked Questions FAQ
1. What is Imamia Students Organization in simple words
Imamia Students Organization is a Shia Muslim students group in Pakistan. It works in schools, colleges, and universities to guide young people in faith, study, and social life.
2. When was ISO founded
ISO was founded on 22 May 1972 at the University of Engineering and Technology UET in Lahore Pakistan.
3. Is ISO only for Shia students
ISO mainly focuses on Shia Muslim students but its public programs like blood camps or seminars are often open to everyone. Many of its messages talk about unity and peace among all Muslims.
4. What are the main goals of ISO
The main goals are to promote Islamic values, strengthen the beliefs of youth, support students in education, and encourage them to serve society. It also tries to build unity and stand against injustice and moral problems.
5. What kind of activities does ISO do
ISO organizes religious gatherings, Quran classes, study circles, blood donation drives, relief work, and student guidance programs. In some regions it also runs exam help classes and career counseling.
6. Is ISO a political party
ISO is not a political party. It is a student and religious organization. It sometimes speaks on social and education issues and may stand with other groups on matters like student rights or justice.
7. Does ISO get money from foreign countries
Some people have claimed that ISO receives money from foreign governments. ISO leaders say that the group is funded by members and supporters inside Pakistan and only receives moral guidance from outside scholars.
8. How can a student join ISO
In most places, a student can contact the local ISO unit at their school, college, or university. They may fill a simple form, attend meetings, and agree to follow the rules and code of conduct of the organization.
9. Where is the head office of ISO
The main head office of ISO often called Al Mustafa House is in Lahore Pakistan.
10. Why is ISO important for Pakistan
ISO is important because it helps many young people grow in faith, education, and social responsibility. Through welfare and education projects, it supports poor students and sick people and gives youth a chance to do positive work for their country.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
Berushbrand com: Easy Guide to Style, Self-Care, and Branding Online

Berushbrand.com is a magazine style website that publishes simple guides and ideas across many topics: style, self care, travel, tech, finance, and more. It looks and reads like a modern WordPress blog with clear categories, a search box, and a “Write For Us” link in the menu. You can also find a contact email in the footer.
What is Berushbrand.com?
At its core, Berushbrand.com is a content site. It groups articles into sections like Business, Travel, Finance, Education, Health, Fashion, Tech, General, and more. The layout is clean and easy to scan, and each post shows a title, an image, the author (“berushbrand”), and a date.
The Tech category page confirms typical WordPress features (archives, categories list, and a “Meta” block that links to WordPress.org). This is a strong sign the site runs on WordPress and follows the familiar blog format many readers already know.
A quick tour of the content
Here are examples of what you’ll find, with real pages you can open:
- General life & relationships – “The Importance of Communication in Every Relationship” (published July 2, 2025). It shares basic tips on better conversations and trust.
- Travel & culture – “Adventure Travel: The Benefits and Risks You Need to Know” explains pros and cons of active trips and how to stay safe (published July 3, 2025).
- Fashion picks – “Top 5 Must-Have Pieces from Fashion to Figure’s Latest Collection” offers a short list of standout items and why they work.
- Health & wellness – The Health section includes simple, short reads like “The Benefits of Using Natural Hair Care Products” and basic fitness advice.
- Tech & learning – “Courses in Information Technology” is an example of beginner friendly content in the Tech category.
Overall, the tone is straightforward and beginner friendly. Articles are short to medium length, with plain words and common sense tips. Posting dates in July–August 2025 show the site is active.

Who the site is for
- Students and new professionals who want simple guides on tech, finance basics, or study tips.
- Style and self care readers who like short lists and basic grooming or fashion ideas.
- Small business or creator audiences who enjoy light articles about tools, social networks, or marketing ideas under the Business and Digital Marketing areas.
How the site is organized
- Top navigation shows major categories, a search field, and a “Write For Us” option (useful if you want to pitch an article).
- Category pages (for example, Tech) include recent posts, an archive by month, and a category list in the sidebar. It looks like a standard WordPress magazine theme.
- Footer lists copyright and a contact email: [email protected]. If you need help or want to contribute, start there.
Strengths at a glance
- Easy to read: short sections, simple wording, and clear headlines.
- Wide range of topics: from travel and fashion to tech and finance, handy for general readers.
- Fresh posts: content dated in mid 2025 suggests current activity.
Things to keep in mind
During checks, some old /shop/ links returned 404 Not Found. If you see third party posts on the web talking about a large store or special products, rely on what you can actually confirm on the official site first. At the time of writing, the live navigation is focused on articles, not a visible store.
If the site adds a shop later, use the tips in the Safety section below before you buy.
Is Berushbrand.com legit?
You can visit the website at an HTTPS address (secure connection) and browse the content and categories directly. For basic contact, use the footer email listed on the site. These are normal signs of a regular blog style site. As with any newer brand, if you decide to buy something or share personal data, follow standard safety steps and look for clear policies on shipping, returns, and privacy.
How to use the site well

- Pick a category that matches your need (for example, Health for simple wellness tips, Tech for beginner guides).
- Use the search box for a quick topic scan (e.g., “education,” “loans,” “IT courses”).
- Check dates to make sure advice is recent. The article pages show the publish date at the top.
- Contact or contribute via the footer email or “Write For Us” if you want to pitch content.
Safety tips (if the site adds a shop or asks for payments)
- Look for “https://” and a lock icon before entering payment details. This means the connection is encrypted (secure), though encryption alone does not prove a site’s reputation.
- Prefer credit cards when paying online; they have stronger protections if an order goes wrong.
- Follow trusted guidance from national cybersecurity bodies on shopping safely online (check the shop is legitimate, only share needed details, and watch for suspicious links).
Pros and cons
Pros
- Simple language and short guides, good for beginners.
- Broad topic mix in one place.
- Clear contact info in the footer.
Cons
- Some legacy /shop/ links now show 404 pages, so e-commerce content (if any) seems incomplete or under change.
- Articles are often general and introductory; advanced readers may want deeper sources.
Final thoughts
Berushbrand.com is best seen today as a reader friendly, WordPress style blog that gathers many lifestyle and learning topics in one place. If you want light, easy content about self care, fashion ideas, basic finance, travel, or beginner tech, it’s a quick stop with simple language and familiar navigation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Berushbrand.com?
Berushbrand.com is a blog style website that shares articles about fashion, self care, travel, finance, tech, education, and more.
2. Who writes the articles on Berushbrand.com?
Most articles are published under the author name “berushbrand.” It is likely run by a small editorial team.
3. Is Berushbrand.com safe to visit?
Yes, the site uses a secure HTTPS connection and can be browsed safely like other blogs.
4. Does Berushbrand.com sell products?
Right now the website focuses on articles. Some old shop links do not work, so it seems there is no active online store at the moment.
5. Can I write for Berushbrand.com?
Yes, the site has a “Write For Us” option in the menu. This means guest writers can pitch articles.
6. What topics are covered on the site?
The main categories are Business, Travel, Finance, Education, Health, Fashion, Tech, and General.
7. Are the articles updated regularly?
Yes, the site shows new posts from July and August 2025, so it is active and updated.
8. Who should read Berushbrand.com?
It is useful for students, young professionals, fashion lovers, and anyone who wants simple guides on lifestyle, learning, or self care.
9. How can I contact Berushbrand.com?
You can use the email given in the site’s footer.
10. Is Berushbrand.com a good source for deep research?
The articles are simple and easy to read. They are good for beginners, but advanced readers may want more detailed sources.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
PLG Supplies: Simplifying Procurement and Logistics for Smarter Business Growth

In today’s competitive marketplace, businesses need more than just quality products they need reliable supply chain partners that simplify procurement, ensure timely delivery, and support long-term growth. PLG Supplies offers exactly that. By combining dependable physical supplies with innovative digital tools, PLG empowers companies across industries to streamline operations, reduce costs, and prepare for the future.
Introduction to PLG Supplies
PLG Supplies stands for Product-Led Growth Supplies, encompassing everything from industrial machinery and power tools to personal protective equipment (PPE), plumbing fixtures, and consumables. These supplies are essential for safe, smooth, and cost-efficient operations in industries such as construction, engineering, manufacturing, utilities, and healthcare.
Unlike traditional procurement, PLG Supplies go beyond just providing materials. They support the entire life cycle of a system—design, installation, upgrades, maintenance, and expansion. This reduces downtime, cuts costs, and ensures that businesses can adapt quickly to changing demands.
Versatility Across Industries
Modern businesses demand flexibility, and PLG Supplies are designed to meet that challenge. Whether it’s heavy construction equipment or advanced digital procurement tools, PLG adapts to the unique needs of different sectors.
This versatility ensures that both large enterprises and smaller businesses benefit equally from dependable supplies, scalable logistics, and high-quality products.
Industries that Benefit from PLG Supplies
PLG Supplies serve a wide range of industries, each with distinct needs:
- Construction – Power tools, machinery, scaffolding, and safety gear keep projects on schedule.
- Manufacturing – Conveyor belts, cleaning products, and industrial-grade fasteners reduce downtime and enhance productivity.
- Engineering – Precision instruments, measuring devices, and electrical components maintain accuracy and system integrity.
- Municipal Projects – From plumbing fittings to safety gear, public infrastructure projects rely on reliable PLG supplies.
- Healthcare – Hospitals depend on PPE, plumbing supplies, and cleaning agents to maintain safe, compliant facilities.
- Food Processing – Certified supplies and hygiene equipment ensure compliance with strict health regulations.
This broad application makes PLG Supplies an indispensable partner for any sector that values reliability, safety, and efficiency.
Key Product Categories
PLG Supplies covers a comprehensive range of products critical for everyday operations:
Construction Tools & Equipment
- Power tools, drills, grinders, saws
- Fasteners: bolts, screws, anchors
- Heavy machinery and scaffolding
Safety & PPE
- Hard hats, safety goggles, and respirators
- Gloves, high-visibility vests, and steel-toe boots
- Hearing protection and fire safety equipment
MRO Supplies (Maintenance, Repair, Operations)
- Cleaning agents, degreasers, sanitizers
- Plumbing valves, pipe fittings, and tools
- Electrical components, wiring, and lighting
Industrial & Mechanical Equipment
- Welding equipment and hydraulic systems
- Pneumatic tools and material handling gear
- Storage solutions and modernization cabinets
These categories cover everything from mission-critical safety gear to everyday consumables, ensuring companies have what they need—when they need it.
Benefits of Deploying PLG Supplies

Investing in PLG Supplies creates measurable advantages:
- Improved Safety – High-quality PPE and certified components reduce workplace accidents and keep teams compliant.
- Cost Savings – Longer-lasting equipment reduces repair frequency, downtime, and emergency purchases.
- Efficiency Gains – Automated digital tools simplify procurement, inventory management, and resource allocation.
- Extended Equipment Life – Certified parts maintain infrastructure and machinery, reducing capital investments.
These benefits translate into stronger operations, happier employees, and healthier bottom lines.
Commitment to Availability and Timely Delivery
In industries where downtime costs thousands per minute, availability and delivery speed are critical. Top PLG suppliers maintain:
- Deep inventory of high-demand and specialty products
- Advanced analytics for demand forecasting
- Strong logistics networks ensuring region-wide delivery
This commitment ensures businesses always have access to critical supplies—no matter the scale of the project.
Competitive Pricing and Partnerships
Cost control is a major factor in supply chain management. PLG Supplies achieves affordability through:
- Direct manufacturer partnerships for better pricing and faster availability
- Bulk order discounts to reduce overall costs
- Tiered pricing and loyalty programs that reward long-term customers
Leading suppliers like Grainger, McMaster-Carr, Fastenal, and Amazon Business all showcase how competitive partnerships make supply chains more resilient and cost-efficient.
Sustainable Options for Tomorrow’s Supply Chains
Sustainability is no longer optional—it’s a requirement. PLG Supplies actively supports eco-friendly practices through:
- Recyclable materials for connectors and packaging
- Biodegradable cleaning products
- High-efficiency lighting and low-energy equipment
By partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, businesses not only meet compliance standards but also reduce their environmental footprint and appeal to eco-conscious clients.
Digital PLG Tools for Modern Supply Chains
Beyond physical goods, PLG integrates digital solutions to optimize procurement:
- Analytics Tools – Predict demand spikes, prevent shortages, and reduce waste.
- Feedback Systems – Real-time user feedback drives product improvements and supplier accountability.
- Onboarding Platforms – Interactive tutorials and digital kits shorten learning curves, ensuring faster adoption of new systems.
These digital innovations merge seamlessly with physical supply chains, enabling smarter decisions and long-term growth.
Why PLG Supplies Are Strategic Assets\

PLG Supplies are more than consumables they are strategic business enablers. Companies that invest in strong PLG networks gain:
- Resilience against supply chain disruptions
- Higher employee safety and satisfaction
- Lower operating costs and downtime
- Evidence of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) commitment
By combining technical excellence with strong partnerships, PLG Supplies help companies stay ahead in an unpredictable market.
Action Steps for Competitive Supply Chains
To assess your supply chain strategy, ask yourself:
- Do you have instant access to critical and emergency supplies?
- Are your MRO categories reducing downtime and maintenance costs?
- Is your supplier helping you meet compliance and sustainability targets?
- Are you using digital tools for analytics, procurement, and onboarding?
- Can you scale quickly without supply chain delays?
If the answer is “no” to any of these, it may be time to rethink your supply strategy and adopt a PLG-first approach.
Shape Your Future With Smarter PLG Supply Choices
Your business is only as strong as the supply chain behind it. PLG Supplies provide the tools, safety, and digital solutions that keep operations safe, efficient, and sustainable.
By choosing suppliers that combine reliability, affordability, and digital innovation, you can reduce costs, boost efficiency, and future-proof your operations.
FAQs
1. What does PLG Supplies mean?
PLG Supplies stands for Product-Led Growth Supplies, which include industrial tools, PPE, consumables, and digital tools that support business operations.
2. Is PLG Supplies a manufacturer or distributor?
Primarily, PLG Supplies acts as a distributor, connecting manufacturers with industries like construction, healthcare, and utilities.
3. Can PLG Supplies be ordered in bulk?
Yes. Businesses can place both small and large-scale orders, with bulk options often including discounts and tailored logistics support.
4. Does PLG Supplies operate internationally?
Some PLG suppliers operate locally, while others provide international shipping and partnerships for global businesses.
5. What makes PLG Supplies unique?
Its combination of wide product range, reliable logistics, competitive pricing, and digital tools sets it apart from traditional suppliers.
6. Are sustainable products available?
Yes, many PLG suppliers offer eco-friendly supplies such as recycled gloves, LED lighting, and biodegradable cleaners.
7. How does PLG improve safety?
Certified PPE and compliant system components protect workers, reduce injuries, and ensure businesses meet safety regulations.
8. Can PLG Supplies help reduce costs?
Absolutely. Quality equipment reduces repair frequency and downtime, while digital tools optimize procurement and inventory management.
9. Do PLG suppliers provide technical support?
Many suppliers offer added services like training, onboarding kits, and customer service support to ensure smooth adoption.
10. Who are some leading PLG suppliers?
Top players include Grainger, Fastenal, McMaster-Carr, Amazon Business, and specialized regional suppliers that offer tailored solutions.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
KZ43X9NNJM65 Code: What It Means and Why It’s Important

In today’s fast-paced digital world, it’s not uncommon to encounter strange alphanumeric codes in various contexts. One such code that has sparked curiosity and generated interest across the internet is KZ43X9NNJM65. While it might look like a random sequence at first glance, it serves a specific function in the digital realm, ranging from tracking codes to cryptographic data, and it might even be a placeholder for some software tools.
What is the KZ43X9NNJM65 Code?
At its core, KZ43X9NNJM65 appears to be a unique identifier used across several fields, from software development to digital marketing. It can be a string that has different uses based on the system or platform where it appears. Let’s explore the potential purposes and meanings behind the code.
1. Tracking Code for Analytics
One of the most common uses of alphanumeric codes like KZ43X9NNJM65 is as a tracking identifier in analytics. Digital marketers and web developers often embed such codes in URLs or embedded in pages to track user interactions, monitor campaigns, and gather essential data about how visitors behave on a website.
For example, if you’ve ever clicked on a link that redirected you to a product page, that link might include a unique code like this one. This helps website owners understand how effective their marketing campaigns are and how users interact with different elements on their pages. By tracking the performance of certain pages or campaigns, businesses can fine-tune their strategies to improve user experience and conversion rates.
2. Software Versioning
In the world of software development, KZ43X9NNJM65 could also represent a version number or build identifier for a specific piece of software. Software developers often use codes like these to mark different iterations of an application. It serves as a reference for identifying updates, debugging, and troubleshooting.
For instance, if a software developer releases an updated version of an app, they may use a unique code for the release. This helps them keep track of the changes and versions, especially in larger systems with complex updates. The code might appear in logs or be referenced in software documentation, indicating that a specific release is live.
3. Cryptographic Hash or Token

Another possibility for KZ43X9NNJM65 is that it is part of an encrypted token or cryptographic hash. Cryptographic technologies are widely used to ensure secure communication and data protection. Codes like these are often used in data transmission, verifying the integrity of information between two parties, ensuring that the data hasn’t been tampered with.
This type of code could be embedded in online transactions, authentication protocols, or data-sharing systems to verify the identity of the parties involved. By encrypting data, businesses can protect sensitive information from hackers or unauthorized access, maintaining the privacy and security of their users.
4. Placeholder or Test String
In some cases, codes like KZ43X9NNJM65 are simply placeholders used during the development or testing phases of a website or app. Developers might insert such strings into forms or temporary links to test the behavior of elements like buttons, links, or interactive content.
These placeholders are often seen during the beta testing of new software or features, where they help developers check the flow of data and monitor the usability of a feature before it is released to the public. While it might not carry any specific significance in these cases, it serves an essential role in ensuring that the system works smoothly.
Why Is the KZ43X9NNJM65 Code Important?

Now that we have an understanding of what the code might represent, it’s time to look into why it’s important in the digital world. The use of such codes is widespread and highly relevant in various industries, from software development to cybersecurity. Below are some reasons why KZ43X9NNJM65 (or similar alphanumeric codes) holds significance.
1. Enhances Data Security
The importance of data security cannot be overstated in today’s digital age. Codes like KZ43X9NNJM65 often appear in cryptographic systems that encrypt sensitive data. By using complex codes and hashing techniques, businesses ensure that data sent between servers and users is protected from unauthorized access. This is especially vital for online banking, e-commerce platforms, and any system involving sensitive personal information.
2. Improves Website and Campaign Tracking
For marketers and business owners, having the ability to track the performance of their website or campaigns is crucial. Codes like KZ43X9NNJM65 help track how effective marketing efforts are in reaching the right audience and achieving specific goals. These identifiers give businesses insight into user behavior, allowing them to optimize campaigns and refine their marketing strategies for better engagement and conversion rates.
3. Optimizes User Experience
Software developers and web designers use codes like these to optimize the user experience on websites and apps. By ensuring that different features and tools are functioning properly, developers can provide a seamless experience for users, ensuring their websites or apps perform as intended. This ultimately leads to higher user satisfaction, better retention, and increased engagement with the platform.
4. Facilitates Software Updates
For developers working with large systems or applications, keeping track of different versions and releases is critical. The KZ43X9NNJM65 code can help identify specific versions or builds, making it easier for developers to troubleshoot problems, implement fixes, and roll out new features to end users.
Conclusion
While the KZ43X9NNJM65 code might seem like just a random sequence, it plays an essential role in the digital world, from tracking and software development to cryptography and data security. Its varied applications demonstrate its significance across different industries, improving user experiences, protecting data, and ensuring systems function smoothly.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About KZ43X9NNJM65
1. What is the KZ43X9NNJM65 code used for?
The KZ43X9NNJM65 code is primarily used as a tracking identifier, software versioning string, or cryptographic token in various digital systems and processes. It helps track user interactions, manage software versions, and protect data in communication.
2. Is KZ43X9NNJM65 related to cryptography?
Yes, it could be a part of a cryptographic hash or token used to ensure secure data transmission between parties. This helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
3. Can KZ43X9NNJM65 be used for tracking website visitors?
Absolutely. Digital marketers often use such codes in URLs or embedded in pages to track user interactions and monitor campaign performance, giving insights into how visitors behave on a website.
4. Is KZ43X9NNJM65 a random sequence?
While it may appear random, this alphanumeric string serves specific functions in digital environments. It is usually generated intentionally for a purpose, such as tracking, data protection, or versioning.
5. Why do developers use codes like KZ43X9NNJM65?
Developers use codes like these to manage software versions, ensure secure data transmission, and test different features during the development phase. It helps streamline the development process and improve the final product.
6. How does KZ43X9NNJM65 help in improving user experience?
By tracking user behavior and ensuring the correct functionality of features, codes like KZ43X9NNJM65 allow developers to optimize the user experience, ensuring a smoother, more reliable interaction with websites or apps.
7. Can KZ43X9NNJM65 be used for e-commerce websites?
Yes, it can be used to track transactions, monitor campaign effectiveness, and ensure that security measures are in place during online shopping experiences.
8. Is KZ43X9NNJM65 associated with any specific company?
There is no clear association with a specific company at this time. The code is more likely to be used across various platforms, depending on the context in which it appears.
9. Can KZ43X9NNJM65 appear on websites without purpose?
While it might appear on some websites during testing or as a placeholder, any appearances outside of these contexts should be monitored to ensure there is no malicious intent behind its use.
10. How can I know if KZ43X9NNJM65 is safe?
If you encounter this code, especially in unfamiliar links, always ensure that the source is trustworthy. For websites or transactions, look for secure connections (HTTPS) and avoid interacting with suspicious links.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
Kotora Melnkalne: A Complete Travel Guide to Montenegro’s Most Beautiful Town

Nestled along the shimmering Adriatic coastline, Kotor is often regarded as one of Montenegro’s most scenic and historically rich towns. With its ancient walls, picturesque bay, and thriving cultural scene, Kotor has long been a favorite destination for travelers seeking a blend of history, adventure, and natural beauty. This guide will take you through everything you need to know about Kotor Melnkalne, a hidden gem in Montenegro that beautifully marries history, culture, and nature.
What is Kotor Melnkalne?
The term “Kotor Melnkalne” evokes both the grandeur of Kotor’s architecture and the surrounding Bay of Kotor (Boka Kotorska), often referred to as the southernmost fjord in Europe. The name “Melnkalne,” which roughly translates to “dark mountain,” references the dramatic mountains that tower over the town, creating a stark contrast between the deep blue waters and the lush green hillsides. The unique geographic location of Kotor and the stunning combination of natural and historical features make it one of Montenegro’s most captivating locations.
A Glimpse into the History of Kotor
Kotor’s history dates back over two millennia, with influences from the Illyrians, Romans, Byzantines, and Venetians. The town’s strategic position along the Adriatic made it a coveted stronghold for several ancient civilizations. Kotor was originally an Illyrian settlement, and it later became a significant Roman port and a key military asset during the Byzantine Empire. In the 15th century, Kotor came under Venetian rule, which greatly influenced its architectural style and urban development.
The town’s fortifications are some of the most well-preserved in the region, with a mix of Romanesque, Gothic, and Renaissance styles. Kotor’s old town has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site due to its cultural significance and architectural splendor. The Venetian influence is still visible in the town’s palaces, churches, and narrow streets that lead to the imposing Kotor Fortress on the hilltop.
Natural Beauty of Kotor Melnkalne

Kotor is known for its natural beauty, with the surrounding Bay of Kotor offering crystal-clear waters and dramatic landscapes. The bay is sheltered by high mountains, which creates a stunning contrast between the sea and the towering cliffs. These mountains, including Mount Lovćen, provide a dramatic backdrop to the town and are perfect for hiking, photography, and exploration.
The Bay of Kotor is home to several small towns, each with its own charm. Perast, for example, is a picturesque village famous for its historical architecture and the iconic Our Lady of the Rocks church, which sits on an artificial island. The bay also offers great opportunities for sailing, swimming, and relaxing along its peaceful shores.
Hiking in the Mountains
One of the best ways to explore the stunning landscapes around Kotor is by hiking up the mountains that surround the town. The Kotor Fortress hike is one of the most popular, offering panoramic views of the town and the bay. The hike is challenging but rewarding, taking you up steep, winding paths to the fortress at the top.
Another popular hiking destination is Mount Lovćen, which is part of the Lovćen National Park. The views from the top are breathtaking, and visitors can explore the park’s diverse flora and fauna while enjoying the pristine nature of Montenegro.
Cultural Heritage and Attractions
Kotor is not just about scenic views; it also boasts a rich cultural and architectural heritage. The town’s Old Town is a maze of narrow streets, charming squares, and historical buildings. Some of the key cultural attractions in Kotor include:
St. Tryphon’s Cathedral
Built in the 12th century, St. Tryphon’s Cathedral is one of the most important landmarks in Kotor. This Romanesque-style cathedral is dedicated to St. Tryphon, the patron saint of Kotor. The cathedral’s bell tower, which offers stunning views of the surrounding area, is one of the most iconic features of the town.
The Maritime Museum
Kotor has a rich maritime history, and the Maritime Museum is the perfect place to learn about it. The museum is located in a beautiful Baroque building and features exhibits on Kotor’s naval history, including model ships, nautical maps, and historic maritime artifacts. It provides a deeper understanding of the town’s significance as a port city.
Kotor’s City Walls and Fortress
The City Walls of Kotor are some of the best-preserved fortifications in the region. Stretching over 4.5 kilometers, these walls were built to protect the town from invaders and are a testament to Kotor’s strategic importance throughout history. The Kotor Fortress, located on the hill above the town, offers an unforgettable view of Kotor and the bay.
Clock Tower
Located in the main square of Kotor’s Old Town, the Clock Tower is a striking feature of the town’s skyline. Built in the 17th century, it remains a significant historical landmark and serves as a reminder of Kotor’s long-standing connection to timekeeping and precision.
Events and Festivals in Kotor
Kotor is also known for its vibrant cultural scene, with numerous events and festivals throughout the year. Some of the most popular events include:
Kotor Carnival
Held in February or March, the Kotor Carnival is one of the town’s biggest events. This colorful celebration features parades, music, dancing, and traditional costumes. It’s a great way to experience the local culture and join in the lively festivities.
Boka Night
One of the most magical events in Kotor, Boka Night, is a celebration of the sea, featuring a procession of illuminated boats that sail through the bay. This event, which takes place in July, brings together locals and tourists for a night of music, dancing, and cultural performances.
St. Tryphon’s Day
Celebrated on February 3rd, St. Tryphon’s Day is a religious and cultural festival honoring Kotor’s patron saint. The day includes a special church service, processions, and various festivities throughout the town.
Travel Tips for Visiting Kotor Melnkalne

Best Time to Visit
The best times to visit Kotor are during the spring (April to June) and fall (September to October). During these months, the weather is mild, and there are fewer tourists, making it easier to explore the town and surrounding areas. The summer months (July and August) are also popular, but the town can get crowded, and prices for accommodation may be higher.
Getting There
Kotor is easily accessible by car, bus, or ferry. The nearest airport is in Tivat, which is about 10 kilometers away from Kotor, while Podgorica Airport is about 80 kilometers away. Many visitors also choose to arrive by boat, as Kotor is a popular port for cruise ships.
Where to Stay
Kotor offers a variety of accommodation options, ranging from luxury hotels to charming guesthouses and private apartments. For a truly unique experience, consider staying in one of the old town’s historic buildings, which offer a glimpse into Kotor’s rich history.
Conclusion
Kotor, with its rich history, stunning landscapes, and vibrant culture, is a must-visit destination for anyone traveling to Montenegro. Whether you’re interested in exploring historical sites, hiking through beautiful mountains, or simply enjoying the natural beauty of the Bay of Kotor, Kotor Melnkalne offers something for everyone. Make sure to add Kotor to your travel bucket list and experience its timeless charm for yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Kotor Melnkalne known for?
Kotor Melnkalne is known for its historical architecture, stunning natural beauty, and its location within the Bay of Kotor, which is often described as Europe’s southernmost fjord. - Is Kotor a UNESCO World Heritage Site?
Yes, Kotor’s Old Town and its surrounding fortifications were designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979 due to their historical significance. - What is the best time to visit Kotor?
The best times to visit are during the spring (April–June) and autumn (September–October), as the weather is pleasant, and there are fewer tourists. - How can I reach Kotor?
Kotor is accessible by car, bus, and boat. The nearest airport is in Tivat, about 10 kilometers away, while the nearest port is also in Kotor. - What are the main attractions in Kotor?
Key attractions include St. Tryphon’s Cathedral, Kotor’s Old Town, Kotor Fortress, the Maritime Museum, and the City Walls. - Is hiking popular in Kotor?
Yes, hiking is a popular activity, especially the Kotor Fortress hike and exploring Mount Lovćen for panoramic views of the bay. - What events are held in Kotor?
Notable events include the Kotor Carnival, Boka Night, and St. Tryphon’s Day. - What is the food like in Kotor?
Kotor offers a variety of local dishes, including seafood, olive oil, cheese, and prosciutto, often paired with local wines. - Can I visit the Bay of Kotor by boat?
Yes, the Bay of Kotor is ideal for boat tours, and visitors can explore nearby islands like Our Lady of the Rocks. - What are the accommodations like in Kotor?
Kotor offers a range of accommodations, from luxury hotels to charming guesthouses, many of which are located within the Old Town for an authentic experience.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
dsnews co uk: Your Trusted Source for UK News and Insights

dsnews co uk is a digital news platform that has quickly earned its place among reliable sources of information for readers seeking up-to-date news and insights. With a range of coverage spanning across politics, technology, business, lifestyle, and more, dsnews co uk is designed to cater to a wide array of readers in the UK and beyond. In this article, we will explore the features of dsnews co uk, how it stands out from other platforms, and why it’s worth your attention.
Introduction to dsnews co uk
In today’s fast-paced world, staying informed is more important than ever. With the abundance of information available on the internet, finding trustworthy and timely news outlets is crucial. dsnews co uk is a platform dedicated to providing reliable, real-time updates across various sectors including business, technology, politics, culture, and health. The site’s mission is to offer balanced reporting, detailed analysis, and easy-to-understand coverage of events, helping readers make sense of the world around them.
What Makes dsnews co uk Stand Out?

One of the key aspects that sets dsnews co uk apart from other news platforms is its commitment to delivering news in a user-friendly manner. With a clean, modern design, the website is easy to navigate, allowing readers to quickly find the latest stories and articles that matter most to them. Let’s dive into some of the defining features that make dsnews co uk a trusted source of news.
1. Diverse Content Coverage
dsnews co uk covers a wide variety of topics, ensuring that there is something for everyone. Whether you’re interested in the latest developments in the UK political scene, the newest trends in tech, or updates on health and lifestyle, dsnews co uk has it all. This breadth of coverage allows readers to stay informed about the most important issues across different fields.
2. Real-Time Updates
In today’s world, timing is everything when it comes to news. dsnews co uk is dedicated to delivering updates as they happen. The site ensures that readers are always informed with the most current developments, whether it’s breaking news or ongoing events. This commitment to real-time reporting ensures that dsnews co uk remains a relevant and up-to-date source for news.
3. In-Depth Analysis and Insight
Beyond just delivering the news, dsnews co uk also provides in-depth analysis and commentary. This feature is especially useful for readers who want to understand the full scope of events and the underlying issues at play. Whether it’s a complex political situation or a business development, dsnews co uk offers the necessary context to help readers grasp the significance of each story.
4. Engagement with Readers
Another standout feature of dsnews co uk is its focus on engaging with readers. Through interactive comment sections, polls, and integration with social media platforms, the website encourages discussions and opinions on the news. This community-driven approach creates a more inclusive and interactive experience for readers, allowing them to share their thoughts and interact with other users.
5. Multimedia Integration
In addition to traditional text-based content, dsnews co uk integrates various forms of multimedia such as videos, images, and infographics. These elements help to illustrate key points in articles, making them more visually appealing and easier to understand. This multimedia approach is especially useful for complex stories that benefit from visual explanations.
6. Mobile-Friendly Design
With a growing number of people consuming news on mobile devices, dsnews co uk has ensured that its platform is optimized for smartphones and tablets. The mobile-friendly design ensures that readers can access content seamlessly, no matter what device they’re using.
Ethical Journalism and Credibility
dsnews co uk adheres to high ethical journalism standards, which is an essential aspect of any trustworthy news platform. It avoids sensationalism, respects privacy, and corrects errors when they occur. By maintaining a focus on integrity, dsnews co uk has earned the trust of its readers and positioned itself as a reliable source for news.
The platform is also committed to fact-checking and providing reliable sources to back up the stories it reports. This is crucial in a world where misinformation can easily spread, and it helps establish dsnews co uk as a reputable news outlet.

Conclusion
dsnews co uk offers a comprehensive news experience, making it an excellent resource for those seeking timely updates and in-depth insights on a wide range of topics. With its commitment to ethical journalism, real-time updates, and multimedia content, the platform has become a trusted source for UK news and analysis. Whether you’re looking for breaking news or in-depth analysis, dsnews co uk provides a user-friendly and reliable solution to stay informed in today’s fast-paced world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about dsnews co uk to help you learn more about the platform:
1. What is dsnews co uk?
dsnews co uk is a UK-based digital news platform that offers timely news updates, analysis, and insights across various sectors including politics, business, health, technology, and lifestyle.
2. What topics does dsnews co uk cover?
The site covers a broad range of topics, including breaking news, politics, business, technology, lifestyle, health, and more. It aims to provide balanced and insightful coverage on a wide variety of issues.
3. Is dsnews co uk a reliable source of news?
Yes, dsnews co uk is committed to ethical journalism practices, including fact-checking, providing credible sources, and offering in-depth analysis. It is known for delivering accurate and timely news.
4. Can I read dsnews co uk on my mobile device?
Yes, dsnews co uk has a mobile-friendly design, allowing users to access the site seamlessly on smartphones and tablets.
5. Does dsnews co uk offer multimedia content?
Yes, dsnews co uk incorporates multimedia elements such as videos, images, and infographics to make articles more engaging and visually informative.
6. How often is dsnews co uk updated?
dsnews co uk is updated in real-time to provide readers with the latest news and developments as they happen.
7. Can I interact with other readers on dsnews co uk?
Yes, the platform includes interactive features like comment sections, polls, and social media integration, encouraging reader engagement and discussion.
8. Does dsnews co uk cover international news?
While dsnews co uk primarily focuses on UK news, it also covers relevant international events, especially those that impact the UK or its citizens.
9. How can I subscribe to dsnews co uk for updates?
You can subscribe to dsnews co uk through the website to receive newsletters or real-time updates on breaking news and important stories.
10. Is dsnews co uk free to access?
Yes, dsnews co uk is free to access. There is no subscription required to read the articles and stay updated with the latest news.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
Unlocking “DGH A”: Decoding Its Meanings & Why It Matters for You

Have you ever come across an acronym that leaves you scratching your head, wondering what on earth it could mean? “DGH A” might just be one of those terms! In today’s fast-paced world, where acronyms and abbreviations are tossed around like confetti, it’s easy to feel lost. But don’t worry, we’re here to demystify “DGH A” and explore its various intriguing meanings.
Depending on the context, “DGH A” can represent vastly different concepts, from the heart of India’s energy sector to crucial aspects of personal finance and even the science of water quality. So, let’s embark on a journey to uncover what “DGH A” could signify and why understanding these distinctions might be more relevant to your life than you think.
Diving Deep: The Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH), India
Perhaps one of the most significant and impactful interpretations of “DGH” (with the “A” potentially referring to its “Activities” or “Areas”) is the Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH) in India. This isn’t just a government body; it’s a pivotal player in India’s energy independence and economic growth.
What is the DGH?

Established in 1993 under the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India, the DGH was created with a clear mandate: to promote and regulate the exploration and production of oil and natural gas within the country. Think of them as the technical backbone of India’s upstream petroleum sector, guiding policies and overseeing operations to ensure the nation’s energy security.
Why is the DGH Important?
The DGH plays a multi-faceted role that touches every aspect of hydrocarbon exploration and production in India. Here’s a closer look at their critical functions:
- Policy Guidance and Technical Advice: The DGH provides expert technical advice to the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas on all strategic matters related to hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation. This includes shaping policies, regulations, and guidelines that govern the entire industry.
- Overseeing Exploration Programs: Before a single drill can penetrate the earth, extensive geological and geophysical studies are conducted. The DGH meticulously reviews the exploration programs submitted by various oil and gas companies, ensuring they are scientifically sound, economically viable, and environmentally responsible.
- Evaluating Hydrocarbon Reserves: Knowing how much oil and gas a country has is crucial for long-term planning. The DGH is responsible for independently assessing and certifying the hydrocarbon reserves across India, providing reliable data for national energy strategies.
- Managing Acreage and Contracts: The process of allocating exploration blocks (acreages) to companies and managing the contracts (like Production Sharing Contracts) is complex. The DGH advises on acreage offerings, monitors compliance with contractual obligations, and ensures fair practices.
- Reviewing Development Plans: Once hydrocarbons are discovered, companies must submit detailed development plans outlining how they intend to extract the resources. The DGH scrutinizes these plans to ensure optimal recovery, technological efficiency, and adherence to safety and environmental standards.
- Data and Sample Preservation: Geological data and core samples are invaluable. The DGH ensures that all data and samples collected during exploration and production activities are properly preserved and archived, serving as a national repository for future studies and research.
- Promoting Unconventional Resources: India’s energy future isn’t just about conventional oil and gas. The DGH is actively involved in exploring and developing unconventional hydrocarbon resources like Coal Bed Methane (CBM), Shale Gas/Oil, and Gas Hydrates, which hold immense potential to diversify the nation’s energy mix.
In essence, the DGH acts as a guardian of India’s hydrocarbon wealth, balancing the need for energy security with responsible resource management and environmental stewardship. If “DGH A” refers to the “Activities” of the Directorate General of Hydrocarbons, it highlights their proactive and comprehensive involvement in shaping India’s energy landscape.
Securing Your Future: “DGH” as a Declaration of Good Health in Insurance
Shifting gears entirely, “DGH” takes on a very personal meaning in the world of insurance: a Declaration of Good Health (DGH). If you’ve ever applied for a life insurance policy, revived a lapsed one, or made changes to an existing plan, you might have encountered this form.
What is a Declaration of Good Health?
An insurance company relies on accurate information about your health to assess risk and determine your premium. A DGH form is essentially a statement signed by you, the applicant or policyholder, confirming that your health status has not significantly changed since your initial application or a specific date.
When is a DGH Form Required?
- Policy Issuance: Sometimes, after the initial application, there might be a delay in issuing the policy. The insurer might require a DGH to confirm that no adverse health events have occurred in the interim.
- Policy Revival: If your insurance policy has lapsed due to unpaid premiums, and you wish to reinstate it, the insurer will almost certainly require a DGH form. This is because your health might have deteriorated since the policy lapsed, and they need to re-evaluate the risk.
- Policy Changes: Certain changes to your policy, such as increasing the sum assured or adding a new rider, might necessitate a DGH to ensure your health still meets the insurer’s criteria for the enhanced coverage.
Why is it Important to be Truthful?

Filling out a DGH form requires honesty and accuracy. Misrepresenting your health status can have serious consequences, potentially leading to:
- Policy Voidance: The insurer might void your policy if they discover a material misrepresentation, meaning your beneficiaries might not receive the death benefit when you pass away.
- Claim Denial: In the event of a claim, the insurer could deny it if they find that you withheld or misrepresented crucial health information.
Therefore, if “DGH A” pops up in an insurance context, it’s a gentle reminder about the importance of transparency and accuracy in securing your financial future and ensuring your loved ones are protected.
The Science of Water: “dGH” as Degrees of General Hardness
From national energy and personal finance, let’s dive into the fascinating world of water chemistry. Here, “dGH” (often written with a lowercase ‘d’ and a degree symbol, °GH) refers to degrees of General Hardness. This term is particularly relevant for aquarists, gardeners, and anyone interested in water quality.
What is General Hardness?
Water hardness is a measure of the concentration of specific mineral ions dissolved in water. General hardness, or GH, specifically quantifies the concentration of divalent metal ions, primarily calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+). These minerals are naturally picked up by water as it flows over rocks and soil.
Understanding the Unit “dGH” or “°GH”
One dGH is defined as 10 milligrams (mg) of calcium oxide (CaO) per liter of water. While calcium oxide itself isn’t what makes water hard, this unit provides a standardized way to measure the total concentration of these hardening ions.
Why Does Water Hardness Matter?
- Aquariums: For fish keepers, water hardness is critical. Different fish species thrive in different hardness levels. For example, discus fish prefer very soft water, while African cichlids require hard water. Incorrect hardness can stress fish, impact their breeding, and affect plant growth in an aquarium.
- Gardening: Plant growth can also be influenced by water hardness. Some plants prefer softer water, while others tolerate or even thrive in harder water.
- Household Use: Hard water can lead to mineral buildup (limescale) in pipes, appliances (like kettles and washing machines), and can reduce the effectiveness of soaps and detergents.
- Drinking Water: While water hardness isn’t generally a health concern for drinking, it can affect the taste of water.
So, if you encounter “dGH A” in a scientific or hobbyist context, especially regarding water, it’s almost certainly referring to the measurement of general hardness, perhaps indicating a specific “Analysis” or “Assessment” of water quality.
The Digital Frontier: “DGH A” as an Emerging Digital Term
In our increasingly digital world, new acronyms and terms are constantly emerging, sometimes without a universally agreed-upon definition. “DGH A” has recently appeared in various online discussions and articles, particularly within digital, tech, and business transformation contexts. While its precise meaning can vary, some prominent interpretations suggest an exciting future:
- Data Governance Hub Architecture (DGH A): This is one of the more compelling emerging interpretations. In an era where data is king, managing it effectively is paramount. A Data Governance Hub Architecture refers to a strategic framework and integrated system that organizations implement to govern their data assets. It encompasses:
- Structured Practices: Establishing clear policies, roles, and responsibilities for data management.
- Data Integration: Connecting various data sources to create a unified and consistent view.
- Compliance and Security: Ensuring data adheres to regulatory requirements (like GDPR or HIPAA) and is protected from unauthorized access.
- Quality Assurance: Maintaining data accuracy, completeness, and reliability.
- Code Name or Project Identifier: Sometimes, “DGH A” might simply be an internal code name for a specific digital project, a new software release (e.g., “Digital Growth Hub Alpha”), or a component within a larger system that is still in its beta phase or under development.
- Business Classification: In large organizations, “DGH A” could serve as a classification or category within a data management system, perhaps denoting a specific “Digital Growth Hub” or a division focused on “Digital Generation & Analytics, Stream A.”
These emerging interpretations highlight the dynamic nature of digital terminology, where new phrases are coined to capture evolving concepts. While not as established as the other meanings, these digital interpretations often point towards themes of advanced algorithms, machine learning, real-time data analysis, and the streamlining of operations through digital means.
The Broader Spectrum: Other Less Common Meanings of DGH
While the above are the most common and impactful meanings, “DGH” (and by extension “DGH A”) can have other, less frequent interpretations depending on specialized contexts:
- District General Hospital: In the UK, “DGH” is a common abbreviation for a District General Hospital, which provides a wide range of secondary care services to a local population. So, “DGH A” could refer to a specific hospital, or perhaps an “Annex” or “Wing A” of such a hospital.
- D. George Harris & Associates: This refers to a company founded in 1988, specializing in environmental services and consulting. In this context, “DGH A” might be a specific project, client, or department within their operations.
- DGH Technology: This company is known for its ultrasonic A-scan devices, particularly used in ophthalmology for measuring eye structures. Here, “DGH A” would likely refer to a specific model or “Series A” of their instruments.
- Dutile, Glines and Higgins Corporation (DGH Corp.): This company is associated with data acquisition modules and related technologies. Similar to the previous examples, “DGH A” could denote a product line, a specific module, or a project.
These examples underscore the importance of context when encountering “DGH A.” Without additional information, pinpointing the exact meaning can be like solving a puzzle.
Conclusion: The Power of Context
As we’ve journeyed through the diverse meanings of “DGH A,” one thing becomes abundantly clear: context is king. An acronym that seems obscure at first glance can unveil critical information about national energy policies, your financial safeguards, the intricate science of water, or the cutting edge of digital transformation.
Whether you’re an industry professional, an insurance policyholder, an avid aquarist, or simply someone curious about the evolving digital landscape, understanding the various interpretations of “DGH A” can equip you with valuable insights. So, the next time you encounter this intriguing abbreviation, you’ll be well-prepared to decode its true meaning and appreciate its significance in whichever world it resides.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are 10 frequently asked questions to help you further understand “DGH A”:
- What is the primary role of the Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH) in India? The DGH primarily provides technical advice to the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India, on matters related to exploration and optimal exploitation of oil and natural gas within the country, ensuring energy security.
- Why would an insurance company ask for a Declaration of Good Health (DGH) form? Insurance companies ask for a DGH form to confirm that an applicant’s or policyholder’s health status has not significantly changed since their initial application or a specific date, especially for policy issuance, revival, or certain policy changes.
- What does “dGH” mean in the context of water quality, and why is it important for aquariums? In water quality, “dGH” (degrees of General Hardness) measures the concentration of divalent metal ions like calcium and magnesium. It’s crucial for aquariums because different fish species and plants thrive in specific hardness levels, and incorrect levels can cause stress or health issues.
- How is one dGH defined in terms of water chemistry? One dGH is defined as 10 milligrams (mg) of calcium oxide (CaO) per liter of water, serving as a standardized unit for measuring total general hardness.
- What is the emerging digital interpretation of “DGH A”? A significant emerging interpretation is “Data Governance Hub Architecture,” which refers to a strategic framework for organizations to effectively manage their data assets, ensuring structure, integration, compliance, and quality.
- Can “DGH A” be an internal code name for a project? Yes, in digital or business contexts, “DGH A” can sometimes be an internal code name for a specific digital project, a new software release (e.g., “Digital Growth Hub Alpha”), or a component within a larger system.
- Is it mandatory to be truthful when filling out an insurance DGH form? Absolutely. Being truthful is mandatory. Misrepresenting your health status can lead to severe consequences, including the voidance of your policy or denial of claims.
- Are there any less common, specialized meanings for DGH? Yes, less common meanings include “District General Hospital” (in the UK), “D. George Harris & Associates” (a company), and “DGH Technology” (related to ultrasonic devices), among others, depending on the specific industry.
- What are unconventional hydrocarbon resources that DGH (India) focuses on? The DGH in India also focuses on exploring and developing unconventional hydrocarbon resources such as Coal Bed Methane (CBM), Shale Gas/Oil, and Gas Hydrates to diversify the nation’s energy mix.
- How can understanding “DGH A” be beneficial to an average person? Understanding “DGH A” can be beneficial because it helps clarify jargon in different fields—from understanding national energy policy, ensuring proper insurance coverage, maintaining a healthy aquarium, or even grasping new concepts in the rapidly evolving digital world.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
Unlocking Your Child’s Potential: Map 2.0 post assessment answers

As parents and educators, we’re all deeply invested in a child’s learning journey. We want to understand their progress, identify areas where they shine, and provide support where they might need a little extra help. In today’s educational landscape, assessments play a crucial role in providing these insights. One assessment that many students encounter is the NWEA MAP Growth test, often referred to in discussions as “MAP 2.0.”
You might have heard about the “MAP 2.0 post assessment answers” and wondered what they are and how to access them. It’s natural to want to see the specific questions your child answered and the correct responses. However, when it comes to the MAP Growth test, the concept of a traditional “answer key” is a bit different. Let’s dive into what the MAP Growth test is all about, why official answer keys aren’t typically provided, and most importantly, how you can understand your child’s results to truly unlock their learning potential.
Understanding the NWEA MAP Growth Test
The Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) Growth test, developed by the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA), is a computer-adaptive assessment. This means that the test adjusts its difficulty based on your child’s responses. If they answer a question correctly, the next question might be a bit more challenging. If they answer incorrectly, the following question might be easier. This adaptive nature allows the test to pinpoint your child’s current academic level more accurately than a fixed-difficulty test.
The MAP Growth test is typically administered multiple times throughout the school year – often in the fall, winter, and spring. This allows educators and parents to track a child’s academic growth over time, hence the name “Growth” test. It’s not designed as a pass or fail exam but rather as a tool to provide valuable information about what your child knows and is ready to learn next.
The test covers several subject areas, primarily:
- Reading: This section assesses various skills, including phonological awareness (especially in younger grades), word recognition, understanding the meaning of words and phrases, comprehension of literary texts (like stories and poems), and comprehension of informational texts (like articles and reports).
- Mathematics: The math portion evaluates a student’s understanding of numbers and operations, measurement and data, geometry, and algebraic thinking. The specific topics covered will vary depending on the grade level.
- Language Usage: This area focuses on grammar, punctuation, capitalization, sentence structure, and vocabulary as they apply to effective written communication.
- Science: In some schools and grade levels, the MAP Growth test may also include a science assessment, covering topics related to life science, physical science, and Earth and space science.
Why You Won’t Find Official “Answer Keys” for MAP Growth
The primary reason NWEA doesn’t release official answer keys for the MAP Growth tests is to maintain the security and integrity of the assessment. Because the test is administered repeatedly to track growth, making the specific questions and answers publicly available would compromise its effectiveness. If students could simply memorize answers, the test would no longer accurately reflect their true understanding and progress. The adaptive nature of the test, where questions are drawn from a large bank and tailored to each student, further complicates the idea of a single, static answer key.
Think of it like this: the goal of the MAP Growth test is to understand where your child is on their individual learning path and how much they’ve progressed. If the answers were readily available, the test would become a measure of memorization rather than a gauge of actual learning and growth.
Decoding Your Child’s MAP Growth Test Results
While you won’t receive a list of correct and incorrect answers, the MAP Growth test provides a wealth of valuable information through its reports. Understanding these reports is key to unlocking your child’s potential. Here’s a breakdown of the key components you’ll typically see:
- RIT Score: The most important number on the MAP Growth report is the Rasch unit (RIT) score. This is a numerical scale that represents a student’s achievement level in a specific subject. The RIT scale is continuous across grades, meaning a RIT score of 180 in reading generally indicates the same level of understanding regardless of the student’s grade level (though expectations and content differ).
- Think of the RIT score like a yardstick for measuring academic growth. You can compare your child’s RIT score from one test administration to the next to see how much they’ve grown.
- RIT Range: Along with the RIT score, you’ll often see a RIT range (e.g., 195-205). This provides a confidence interval around your child’s score, acknowledging that no test is a perfect measure. It indicates the likely range within which your child’s true score falls.
- Percentile Range: This indicates how your child performed compared to other students in the same grade level nationally who took the MAP Growth test in the same testing window. For example, if your child’s percentile range is 60-75, it means they scored as well as or better than 60 to 75 percent of their peers nationally.
- It’s important to remember that percentiles compare your child to a large group. Focus primarily on your child’s RIT score and their individual growth over time rather than solely on their percentile ranking.
- Lexile Range (for Reading): In the reading section, you might also see a Lexile range. Lexile is a measure of reading ability and text difficulty. This range can help you choose books that are appropriately challenging for your child.
- Growth Projections: MAP Growth reports often include projections of how your child might perform on future tests based on their current growth trajectory. These are not guarantees but can provide a general idea of expected progress.
- Goal Area Performance: The reports usually break down performance by specific goal areas within each subject. For example, in reading, these might include “Literature,” “Informational Text,” and “Vocabulary.” In math, they could be “Operations and Algebraic Thinking,” “Number and Operations in Base Ten,” and “Measurement and Data.” This provides insights into your child’s strengths and areas where they might need more focused instruction.
Using MAP Growth Results to Support Your Child’s Learning
The real power of the MAP Growth test lies not in the individual answers but in the insights the reports provide. Here’s how you can use this information to support your child’s learning:
- Have a Conversation with Your Child’s Teacher: Your child’s teacher is the best resource for understanding their MAP Growth results in the context of their classroom performance and curriculum. Discuss the RIT scores, growth, and goal area performance. Ask how the teacher is using this information to tailor instruction in the classroom.
- Identify Strengths and Areas for Growth: The goal area breakdown can highlight subjects or specific skills where your child excels and areas where they might need additional support. This can help guide conversations with your child about their learning and where they might focus their efforts.
- Set Realistic Goals: By looking at past growth and projections, you can work with your child and their teacher to set achievable learning goals for the future. Focus on growth rather than just reaching a specific score.
- Inform Home Learning Activities: Understanding your child’s strengths and areas for growth can help you choose appropriate learning activities at home. For example, if their reading report indicates a need for improvement in informational text comprehension, you might encourage them to read more non-fiction books and discuss the main ideas. The Lexile range can also guide your book selections.
- Track Progress Over Time: The longitudinal data from multiple MAP Growth test administrations provides a valuable picture of your child’s academic journey. Celebrate their growth and work together to address any areas where progress might be slower.
- Don’t Compare Your Child to Others: Remember that the MAP Growth test is primarily a measure of individual growth. Focus on your child’s progress relative to their own previous performance rather than comparing them to their peers. Every child learns at their own pace.
The Importance of a Holistic View
While MAP Growth results provide valuable data, it’s crucial to remember that they are just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to understanding your child’s overall academic development and potential. Consider these results alongside classroom grades, teacher observations, participation in class, homework completion, and your child’s own enthusiasm for learning. A holistic view will provide a more complete and accurate picture of their progress.
In conclusion, while the specific “MAP 2.0 post assessment answers” in the traditional sense aren’t made available, the detailed reports generated after the MAP Growth test offer a wealth of information about your child’s academic standing and growth. By understanding the RIT score, percentile ranges, goal area performance, and growth projections, and by working collaboratively with your child’s teacher, you can effectively decode these results and use them to unlock your child’s full learning potential. The focus should always be on growth, understanding, and providing the right support to help your child thrive on their educational journey.
Frequently Asked Questions About MAP Growth Test Results
Here are some common questions parents and educators have about MAP Growth test results:
- What exactly is a RIT score, and how should I interpret it?
- A RIT (Rasch unit) score is a numerical value that represents a student’s achievement level on the MAP Growth test in a specific subject. It’s like a continuous ruler that spans across grade levels. A higher RIT score generally indicates a higher level of understanding. You should look at how your child’s RIT score changes over time to see their academic growth.
- Why can’t I see the specific questions my child answered and the correct answers?
- NWEA keeps the specific test questions and answers secure to maintain the integrity and validity of the MAP Growth assessment. If this information were publicly available, it could compromise the test’s ability to accurately measure student growth over time.
- What’s the difference between a RIT score and a percentile rank?
- A RIT score measures your child’s absolute achievement level on a continuous scale. A percentile rank compares your child’s performance to that of other students in the same grade level nationally who took the test around the same time. A percentile of 70 means your child scored as well as or better than 70% of their peers.
- My child’s percentile rank went down, but their RIT score went up. How is that possible?
- This can happen if your child is still growing academically (as indicated by the increased RIT score), but their rate of growth is slower than that of their national peers. It’s important to focus on the RIT score and individual growth as the primary indicators of progress.
- How often will my child take the MAP Growth test?
- Typically, students take the MAP Growth test two to three times per year: in the fall, winter, and spring. The frequency can vary slightly depending on the school or district.
- What are the goal areas in the MAP Growth report, and why are they important?
- Goal areas are specific sub-skills within each subject that the MAP Growth test assesses. For example, in reading, goal areas might include “Literature” and “Informational Text.” Understanding your child’s performance in these areas can help identify specific strengths and weaknesses, allowing for more targeted instruction and support.
- How can I use my child’s MAP Growth report to help them at home?
- Discuss the results with your child and their teacher. Focus on celebrating growth and identifying areas where they can improve. You can use the goal area information to guide your choices of books and learning activities at home. The Lexile range in reading can help you select appropriately challenging books.
- Are MAP Growth scores used for high-stakes decisions like grade promotion?
- Generally, MAP Growth tests are designed to inform instruction and track growth, not for high-stakes decisions like grade promotion or graduation. However, some schools might use them as one of several data points. It’s best to clarify your school’s specific policies.
- Where can I find more information about the NWEA MAP Growth test?
- The official NWEA website (https://www.nwea.org/) is the best source for detailed information about the MAP Growth test, including resources for parents and educators.
- My child was sick on the day of the test, or I feel they didn’t take it seriously. How reliable are these results?
- While MAP Growth is a reliable assessment, individual test scores can be affected by factors like illness, fatigue, or lack of motivation. If you have concerns about the validity of your child’s results, discuss them with their teacher. They may consider this context when interpreting the scores and might recommend a retest if appropriate.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
Exploring Iceporncasting: An Innovative Technique in Art and Design

Iceporncasting is an intriguing and innovative technique that has recently begun to capture the attention of artists and designers worldwide. The term, though relatively new, refers to a method of combining ice and casting techniques to create art pieces with an element of fragility and transformation. This technique merges the worlds of sculpture, temporary art, and environmental interactions. In this article, we will explore what iceporncasting is, its significance in art and design, its applications, and why it is becoming increasingly popular in creative circles.
What is Iceporncasting?
Iceporncasting is a modern approach to casting that uses ice as the primary medium for creating sculptures, designs, and artworks. The term “Iceporncasting” can be broken down into two key elements: “ice” and “casting.” Ice, in this context, is used to create an initial form or mold, which is then cast with materials such as metals, resins, or concrete. The process is distinct because it involves the melting of the ice during or after the creation of the piece, leaving behind a temporary but visually striking form.
The technique offers a sense of ephemerality and unpredictability, as the ice will melt away, leaving behind a trace of its presence in the form of the cast. Artists using iceporncasting are often intrigued by the impermanence of their work, the way it interacts with environmental factors, and the ways in which it challenges traditional concepts of permanence in art.
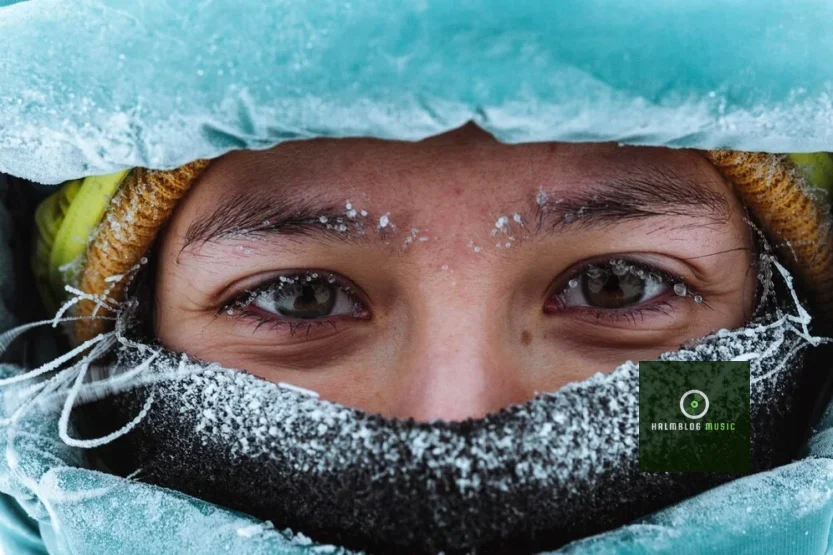

The Technique: How Does Iceporncasting Work?
The process of creating artwork through iceporncasting typically follows these general steps:
- Ice Mold Creation: The first step involves creating a mold or sculpture from ice. This is typically done by freezing water in a container or using custom-made ice molds to shape the ice into specific forms. Artists may carve or shape the ice further to achieve the desired aesthetic.
- Casting Process: Once the ice mold is ready, artists pour a casting material such as molten metal, resin, or concrete into the mold. This step is critical, as the material used will dictate the final appearance and texture of the artwork.
- Melting and Transformation: After the casting material has cooled or set, the ice is allowed to melt, leaving behind the cast object. In some cases, artists may accelerate the melting process, while in others, they may allow the ice to melt naturally. This process adds a sense of temporality to the artwork, as the ice disappears, and only the permanent cast remains.
- Final Touches: After the ice has melted away, the cast piece may be polished, cleaned, or treated further to enhance its appearance or ensure its longevity. The final product can range from delicate sculptures to functional objects with artistic value.
The Appeal of Iceporncasting in Art
There are several reasons why iceporncasting has captured the attention of artists and designers in recent years:
- Ephemeral Nature: One of the main attractions of iceporncasting is the transient nature of the ice. Unlike traditional sculptures or castings, which remain static, the ice in iceporncasting melts away over time. This fleeting quality challenges traditional notions of permanence in art and allows for an ongoing dialogue between the artwork and its environment.
- Environmental Interaction: Iceporncasting is particularly unique because it involves interaction with the surrounding environment. Factors like temperature, humidity, and air circulation all influence how the ice will melt, which can affect the final piece’s appearance. Artists often embrace these variables, knowing that no two pieces will be identical.
- Creative Freedom: The process of iceporncasting allows artists to experiment with the combination of different materials and techniques. The temporary nature of the ice mold provides a unique opportunity to explore new textures and finishes that are not achievable with other mediums.
- Sustainability: Many artists and designers are attracted to iceporncasting because of its environmentally friendly aspects. Ice is a natural, renewable material, and using it in the creative process reduces the need for more traditional, non-sustainable materials. Additionally, since the ice melts away, it doesn’t create long-term waste.
Applications of Iceporncasting in Design

While the most common application of iceporncasting is in art, the technique is also finding its place in design fields such as architecture, fashion, and product design. The following are a few key areas where iceporncasting is being used:
- Sculpture and Installations: Artists are using iceporncasting to create temporary outdoor sculptures or installations. These pieces are often displayed in public spaces or art galleries, where their melting nature can evoke a sense of impermanence and beauty.
- Furniture Design: In the world of interior design, iceporncasting has been explored to create innovative furniture pieces. Designers use ice molds to create intricate patterns in chairs, tables, and lamps, which are then cast with more durable materials like resin or concrete.
- Fashion and Accessories: The fashion industry has also seen the potential of iceporncasting. Jewelry designers and fashion artists use the technique to create unique, one-of-a-kind pieces. The fluidity and transparency of ice make it a compelling medium for crafting innovative, delicate designs.
- Architectural Design: In architecture, iceporncasting has been used to create temporary structures or installations for events like exhibitions or festivals. The technique allows architects to experiment with fluid forms and structures that are not possible with traditional materials.
Challenges and Limitations of Iceporncasting
While iceporncasting offers many exciting possibilities for artists and designers, it is not without its challenges:
- Temperature Sensitivity: The process is highly dependent on temperature, meaning that artists must work in controlled environments to ensure that the ice freezes and melts in the desired way. In outdoor settings, temperature fluctuations can lead to unpredictable results.
- Time Constraints: Since the ice is temporary, artists must work within a limited timeframe. This time-sensitive nature of the medium can be both a challenge and an advantage, as it forces artists to work quickly and creatively.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right casting material is crucial, as it affects the durability and aesthetic of the final piece. Some materials may not be as effective in capturing fine details, while others may not hold up well once the ice has melted.
The Future of Iceporncasting in Art and Design
As artists continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with new materials and techniques, iceporncasting is expected to grow in popularity. The unique combination of art and environmental interaction makes it a perfect medium for artists who seek to explore themes of impermanence, change, and the interplay between nature and design.
Moreover, as more people become aware of sustainable design practices, iceporncasting’s use of natural materials will likely make it an appealing choice for eco-conscious creatives.
Conclusion
Iceporncasting is a fascinating technique that blends creativity, impermanence, and environmental interaction. Its unique combination of ice, casting materials, and the forces of nature offers an exciting frontier for artists and designers looking to explore new ways of creating art. Whether you’re a budding artist, a seasoned designer, or simply someone interested in innovative artistic processes, iceporncasting represents a fresh and thought-provoking way to approach creativity in the modern world.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is iceporncasting?
Iceporncasting is an artistic technique that uses ice as a mold for casting other materials, such as metals or resins. The ice melts away, leaving behind a permanent cast. - Why is ice used in this technique?
Ice is used because it is a natural material that is easily shaped and melts away, providing a temporary medium for creating sculptures and designs. - Can iceporncasting be used in outdoor settings?
Yes, iceporncasting can be used outdoors, but artists must account for temperature changes that can affect the melting process. - What materials are typically used in the casting process?
Common materials for casting include molten metal, concrete, resin, and other durable substances that can capture the details of the ice mold. - What makes iceporncasting unique?
The unique aspect of iceporncasting is its ephemeral nature, where the ice melts away, leaving behind a permanent cast. This creates a sense of temporality in art. - What challenges do artists face when using this technique?
Temperature sensitivity, time constraints, and material selection are some of the challenges artists face when working with iceporncasting. - Is iceporncasting environmentally friendly?
Yes, ice is a natural and renewable material, making it an eco-friendly option for artists who seek sustainable practices. - What kind of art can be created with iceporncasting?
Iceporncasting can be used to create sculptures, furniture, jewelry, and even architectural installations. - Where can I see iceporncasting in action?
Iceporncasting is typically showcased in galleries, public installations, and outdoor art exhibitions. - How can I learn more about iceporncasting?
To learn more, consider researching art studios, design workshops, or exhibitions that focus on experimental techniques and the use of ice in art.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
News
Understanding “Fascisterne”: A Simple Guide

The term “Fascisterne” might sound complex, but it simply refers to followers of fascism, a political idea that gained a lot of power in the early 20th century. It’s a topic that’s important to understand because its influence shaped much of modern history and continues to have echoes in our world today. This article will help you grasp what “Fascisterne” means, where it came from, who was involved, and its lasting impact, all in an easy-to-understand way.
What is “Fascisterne” and Where Did It Come From?
When we talk about “Fascisterne,” we’re talking about people who supported or were part of a political movement called fascism. This idea first appeared in the early 1900s, especially in Italy, after the end of World War I. This was a time of great change and difficulty for many countries. The war had left behind a feeling of disappointment and a lot of instability. Economies were struggling, and there was a lot of social unrest. People were looking for solutions, and this created a fertile ground for new, sometimes extreme, ideas to grow.
Benito Mussolini was a very important person in the development of fascism in Italy. He mixed strong feelings of national pride (nationalism) with ideas that were against socialism (anti-socialist sentiments). He presented fascism as a way to fix the problems and chaos in society. His ideas became popular because many people were unhappy with their governments at the time.
As fascism became stronger in Italy, similar ideas started to spread across Europe. Other influential leaders, like Adolf Hitler in Germany, adopted similar principles. They adjusted these ideas to fit their own countries’ situations. The movement appealed to people who wanted strong leadership and a sense of direction when things felt uncertain. Fascist parties were very good at using people’s fears and resentments to gain support. They used propaganda, which is a way of spreading ideas to influence opinions, to get popular backing.
The Core Ideas and Characteristics of Fascism

Fascism is built on a few main ideas that shape how it views the world:
- The State is Supreme: A central belief in fascism is that the state, meaning the country and its government, is more important than individual people’s rights. The idea is that everyone should put the group’s identity and loyalty to the state first.
- Strong, Authoritarian Leadership: Fascist systems rely on a very strong leader who has almost all the power. This leader becomes a symbol of the nation’s strength and guides the country. In such systems, people are generally not allowed to disagree or speak out against the leader.
- Intense Nationalism: This is a key part of fascism. It means having a very deep sense of pride and loyalty to one’s nation, often at the expense of other nations. National identity becomes extremely important, which can lead to treating outsiders or minorities badly.
- Total Control (Totalitarianism): Fascist governments try to control every part of life, not just politics. This includes things like education, media, and even people’s personal lives. The goal is to create a country where everyone thinks and acts according to the government’s ideas, and individual differences are not encouraged.
- Emphasis on Strength and Action: Fascism often promotes ideas of national strength, military power, and the importance of action, even if it means using force. This can lead to aggressive policies and a belief that stronger nations have a right to dominate weaker ones, sometimes linked to a flawed idea called Social Darwinism.
- Use of Propaganda: Fascist regimes heavily rely on propaganda to shape what people think and feel. This involves carefully creating messages, using powerful images, and controlling information to get people to support their ideas. Children are often taught these ideas from a young age to make sure they become part of the country’s culture.
These characteristics show how fascist systems tried to create a highly unified and controlled society, often through fear and the suppression of different opinions.

Key Figures Associated with “Fascisterne”
While Benito Mussolini and Adolf Hitler are the most prominent figures, many others played roles in fascist or similar movements, either by leading them or fighting against them.
- Benito Mussolini (Italy): As the founder of Italian Fascism, Mussolini became prime minister in 1922 and gradually built a totalitarian state. He introduced policies that emphasized national unity, military strength, and economic self-sufficiency, often using propaganda and suppressing opposition.
- Adolf Hitler (Germany): Leader of the Nazi Party, Hitler adapted many fascist principles to create Nazism in Germany. His regime was characterized by extreme nationalism, racial ideology (especially antisemitism), militarism, and expansionist goals that led to World War II and the Holocaust.
Beyond these well-known figures, there were also many individuals who actively resisted fascist ideologies. For example, during the Spanish Civil War, many young people from different countries, including Danes like Harald, Kai, and Aage Nielsen and Hans Petersen, went to Spain to fight against fascism. They believed it was important to stand up against these ideas, even at great personal risk. This shows that while fascism gained power, there were also strong movements of resistance.
How Did “Fascisterne” Rise to Power?
The rise of “Fascisterne” to power in different countries wasn’t always the same, but there were common patterns:
- Exploiting Instability: As mentioned, the aftermath of World War I left many countries in a state of chaos. Economic problems, unemployment, and social unrest made people desperate for solutions. Fascist leaders stepped in, promising to restore order and make their nations strong again.
- Creating an “Us vs. Them” Mentality: Fascist leaders often pointed fingers at specific groups (like minorities or political opponents) and blamed them for the country’s problems. This created a sense of “us versus them” and helped to unite a group of followers against a common enemy.
- Effective Propaganda: Fascist movements were masters of propaganda. They used newspapers, radio, and public speeches to spread their messages, often filled with emotional appeals, false information, and exaggerated promises. They controlled the narrative and silenced opposing voices.
- Paramilitary Violence: In many cases, fascist groups had armed wings or militias (like Mussolini’s Blackshirts or Hitler’s Stormtroopers). These groups used violence and intimidation against political opponents, trade unions, and minority groups, creating fear and weakening resistance.
- Weak Democratic Institutions: In countries where democratic governments were weak or ineffective, fascism found it easier to take hold. People lost faith in traditional politics, opening the door for radical alternatives.
- Appealing to Different Groups: While often supported by the middle class, fascist movements tried to appeal to a broad range of people, including workers who were unhappy with their conditions and even parts of the elite who feared socialist revolutions. They promised to protect national interests and restore traditional values.
In Italy, Mussolini’s Fascist Party used intimidation and political maneuvering to gain influence, eventually leading to his appointment as Prime Minister. In Germany, Hitler’s Nazi Party grew its support through powerful rallies, propaganda, and by exploiting economic despair and national humiliation after World War I.
The Impacts and Consequences of Fascism
The impact of “Fascisterne” on society and politics was profound and often devastating:
- Loss of Freedoms: Under fascist rule, individual freedoms like freedom of speech, assembly, and the press were severely limited or completely abolished. Citizens were expected to conform to the state’s ideology.
- Human Rights Violations: Fascist regimes were responsible for widespread human rights abuses, including imprisonment, torture, and murder of political opponents, minorities, and anyone deemed “undesirable.” The Holocaust, perpetrated by Nazi Germany, is a horrific example of this.
- Aggressive Foreign Policies and War: Nationalism and militarism often led to aggressive expansionist policies. Fascist countries, particularly Germany and Italy, embarked on territorial conquests, which directly contributed to the outbreak of World War II, a conflict that caused unimaginable destruction and loss of life globally.
- Economic Control and State Intervention: Fascist governments often exerted significant control over the economy, aiming for self-sufficiency and directing industries to serve state goals, especially military production.
- Cultural and Social Transformation: Art, literature, and education were heavily controlled and used to promote the state’s ideology. Gender roles became rigid, emphasizing traditional family structures and military service. Trust in institutions like media and government eroded as propaganda became the norm.
- Division and Distrust: Within societies, fascist tactics created deep divisions and distrust. The “us versus them” mentality fractured communities, leading to conflict and hatred.
The period of fascist dominance in Europe left deep scars and fundamentally reshaped the global political landscape.
Common Misconceptions about “Fascisterne”
There are a few common misunderstandings about fascism that are good to clarify:
- Fascism is just another form of extreme right-wing politics: While fascism is on the far right of the political spectrum, it has unique characteristics that set it apart. It’s not just about conservative ideas; it involves a specific combination of totalitarian control, intense nationalism, and the use of violence to achieve its goals.
- Fascism only happens in economically depressed times: While economic hardship certainly provided fertile ground for fascism to rise, it’s not the only factor. Social unrest, political instability, and a desire for strong leadership can also contribute, even in more prosperous times.
- Fascism is only about one leader: While a charismatic leader is often central to fascist movements, the ideology is supported by a broader structure of party members, paramilitary groups, and propaganda machines. It’s a system, not just one person.
- Fascism and Communism are the same: This is a significant misconception. While both are totalitarian, they have fundamentally different ideologies. Communism is based on class struggle and aims for a classless society with collective ownership, while fascism emphasizes national unity, traditional social hierarchies, and private ownership within a state-controlled economy. They were, in fact, often bitter enemies.
The Legacy of “Fascisterne” Today
Even though the major fascist regimes of the 20th century are gone, the legacy of “Fascisterne” continues to be felt and discussed today.
- Historical Warning: The horrors of World War II and the atrocities committed by fascist regimes serve as a powerful historical warning about the dangers of unchecked power, extreme nationalism, and the suppression of human rights.
- Resurgence of Extreme Ideas: In various parts of the world, we sometimes see political movements that show similar tendencies to historical fascism. These might include strong nationalistic sentiments, anti-immigrant rhetoric, the demonization of minority groups, and an appeal to authoritarian leadership.
- Importance of Democratic Values: The experience with fascism has reinforced the importance of strong democratic institutions, protection of individual liberties, freedom of the press, and an active, informed citizenry to resist such movements.
- Contested History: In some regions, the legacy of fascism remains a contested topic, with ongoing debates about how to remember and learn from this difficult period of history.
Understanding “Fascisterne” isn’t just about looking back at the past; it’s about recognizing the patterns and dangers of certain political approaches so we can work towards a more peaceful and just future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does “Fascisterne” literally mean? “Fascisterne” is a Danish term that means “the fascists.” It refers to the people who follow the ideology of fascism.
2. Is fascism the same as Nazism? While Nazism (National Socialism) shared many characteristics with fascism, such as totalitarian control, nationalism, and authoritarianism, it was distinct due to its extreme racial ideology, particularly antisemitism, which was central to its beliefs and policies. Nazism can be seen as a specific, more extreme form of fascism.
3. Why did people support fascism? People supported fascism for various reasons. Many were desperate for stability and order during times of economic hardship and social unrest. Fascist leaders promised strong leadership, national pride, and a return to traditional values. Propaganda and the creation of “enemies” also played a significant role in uniting support.
4. How did fascism deal with the economy? Fascist regimes typically asserted strong state control over the economy, prioritizing national interests and often military production. While they didn’t abolish private property entirely (unlike communism), they heavily regulated industries and directed economic activity to serve the state’s goals.
5. What role did propaganda play in fascism? Propaganda was absolutely crucial for fascist movements. It was used to shape public opinion, promote the leader and the state’s ideology, demonize opponents, and create a sense of national unity and purpose. They used all available media, from newspapers and radio to rallies and art.
6. Did fascism involve violence? Yes, violence was a common tool for fascist movements and regimes. They used paramilitary groups to intimidate political opponents, suppress dissent, and enforce their will. This often escalated into widespread human rights abuses and state-sponsored terror.
7. Is fascism left-wing or right-wing? Fascism is generally considered a far-right political ideology. While it might have some elements that seem to cross traditional political lines (like state intervention in the economy), its core tenets of extreme nationalism, authoritarianism, hierarchy, and opposition to both liberal democracy and communism firmly place it on the right.
8. Are there still fascist movements today? While classical fascist regimes no longer exist, elements of fascist ideology and tactics can be observed in various extreme nationalist, authoritarian, or neo-fascist groups around the world. These groups often promote similar themes of national purity, anti-immigrant sentiment, and strong leadership.
9. How did fascism contribute to World War II? Fascist regimes, particularly Nazi Germany under Hitler and Fascist Italy under Mussolini, pursued aggressive expansionist foreign policies driven by intense nationalism and militarism. Their invasions and alliances directly led to the outbreak and escalation of World War II.
10. What can we learn from understanding fascism? Learning about fascism helps us recognize the dangers of political extremism, the importance of protecting democratic values and human rights, the need for critical thinking about propaganda, and the devastating consequences that can arise when societies succumb to divisive ideologies and authoritarian rule.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoIndia Rose Brittenham: All You Need to Know About Heather Thomas’ Daughter
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoMargot Rooker: All You Need to Know About Michael Rooker’s Wife
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoRobert Noah? All You Need to Know About Trevor Noah’s Father
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoNadia Farmiga? All You Need to Know About Taissa Farmiga’s Sister
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoJackie Witte? All You Need to Know About Paul Newman’s First Wife
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoCheryl Pistono? All You Need to Know About Kareem Abdul-Jabbar’s Ex-Girlfriend
-

 Celebrity9 months ago
Celebrity9 months agoWho is the Father of Jay-Z? Biography of Adnis Reeves
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoAbigail S. Koppel? All You Need to Know About Leslie Wexner’s Wife













