Tech
AI SaaS Product Classification Criteria: Your Guide to Smarter Business Solutions

The world of business is constantly evolving, and at its heart, a powerful force is reshaping how we operate: Artificial Intelligence (AI) delivered as Software as a Service (SaaS). These innovative solutions are no longer just a futuristic concept; they are becoming essential tools for companies of all sizes, offering remarkable opportunities for efficiency, growth, and enhanced customer experiences.
But with a seemingly endless array of AI SaaS products emerging, how do you make sense of it all? How do you choose the right tools that truly align with your specific business needs? The key lies in understanding the various classification criteria that help us categorize and evaluate these sophisticated solutions. This guide will walk you through these essential criteria, empowering you to navigate the AI SaaS landscape with confidence.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Underlying AI Technology
At the core of every AI SaaS product is a specific type of artificial intelligence. Recognizing these fundamental technologies is the first step in understanding what a product is truly designed to do.
Machine Learning (ML) & Predictive Analytics
Think of these as the crystal ball for your business. ML algorithms analyze vast amounts of historical data, identifying intricate patterns and relationships that human eyes might miss. This allows AI SaaS products leveraging ML to make surprisingly accurate predictions about future events.
- Predicting Future Trends: Imagine knowing which customers are likely to leave next month, or what your sales figures will look like in the next quarter. Predictive analytics, powered by ML, makes this possible. This can revolutionize areas like churn prediction, revenue forecasting, and lead scoring, allowing businesses to proactively address potential issues or seize emerging opportunities.
- Optimizing Performance: ML can also optimize various business processes. Dynamic pricing models, for instance, adjust prices in real-time based on demand, inventory, and competitor pricing, maximizing revenue. Similarly, ML can optimize resource allocation, ensuring your teams and assets are used most effectively.
- Continuous Improvement: A remarkable aspect of ML is its ability to learn and improve over time. As these systems are fed more data and observe outcomes, their predictions become more accurate and their insights more refined. This means your AI-powered SaaS tools get smarter the more you use them, providing an ever-increasing return on investment.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Conversational AI

These technologies are all about understanding and interacting with human language, whether written or spoken. They bridge the gap between complex data and human communication, making interactions more natural and efficient.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Perhaps the most visible application, conversational AI powers intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants that can handle customer inquiries, provide instant support, and even guide users through complex tasks. This significantly improves customer service by offering immediate assistance and reducing the burden on human agents.
- Semantic Search and Content Analysis: NLP allows systems to understand the meaning and context of text, enabling more relevant search results within vast document repositories. It also facilitates sentiment analysis, helping businesses gauge customer feelings about their products or services from reviews and social media mentions.
- Automated Summarization and Generation: Imagine automatically summarizing lengthy reports or generating customized email responses. NLP-powered tools can do exactly that, freeing up valuable time for employees and ensuring consistent communication.
Generative AI (Large Language Models & Vision Models)
Generative AI is the creative powerhouse of the AI world. It’s about creating entirely new content – be it text, code, images, or even designs – by learning from massive datasets.
- Automated Content Creation: From marketing copy and blog posts to personalized email templates and product descriptions, generative AI can produce high-quality written content at scale. This can drastically reduce the time and effort spent on content creation, allowing marketing and sales teams to focus on strategy and engagement.
- Code Generation and Development Assistance: Developers are increasingly using generative AI to assist with coding, suggest solutions, and even generate entire code snippets. This can accelerate development cycles and improve code quality.
- Visual Content Creation: Generative vision models can create stunning images, graphics, and even product designs from simple text prompts. This opens up new possibilities for marketing, design, and product visualization.
Computer Vision
Computer vision equips AI SaaS products with the ability to “see” and interpret visual information from images and videos.
- Object Detection and Recognition: This is crucial for tasks like inventory management, security surveillance, and quality control in manufacturing. Systems can automatically identify and track specific objects, ensuring accuracy and detecting anomalies.
- Facial Recognition: Used for security, access control, and even personalized customer experiences in retail, facial recognition technology is becoming increasingly sophisticated.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Applications: Computer vision powers many AR features, such as virtual product try-ons in e-commerce or interactive guides in industrial settings.
Deep Learning
Often considered a specialized subset of machine learning, deep learning uses neural networks with many layers to learn highly complex patterns. It’s particularly effective for tasks requiring a deep understanding of data, such as advanced image recognition, complex natural language understanding, and highly accurate forecasting in dynamic environments. Many of the generative AI models mentioned above rely heavily on deep learning.
Beyond the Tech: Application and Use Case
While understanding the core AI technology is crucial, the true value of an AI SaaS product often lies in its specific application within a business context. Products can be categorized by the problems they solve and the departments they serve.
- Marketing & Sales: This category includes tools for hyper-personalization, customer segmentation, lead generation and scoring, predictive analytics for sales opportunities, and automated content creation for campaigns.
- Customer Service: Think chatbots, intelligent FAQs, automated support ticket routing, and sentiment analysis tools that help customer service teams understand and respond to customer emotions.
- Operations & Efficiency: These solutions focus on streamlining internal processes, such as intelligent automation (often integrating with Robotic Process Automation – RPA), predictive maintenance for machinery, supply chain optimization, and real-time analytics for operational insights.
- Security & Compliance: AI-driven threat detection, fraud prevention systems, automated cybersecurity monitoring, and tools for ensuring compliance with industry regulations fall into this critical category.
- Product Development: AI-assisted development tools, no-code/low-code platforms enhanced with AI, and user behavior analysis for recommending new features or improvements.
- Data Management: Solutions that automate data cleaning, deduplication, product categorization, and data enrichment, ensuring high-quality data for all other AI applications.
The Bottom Line: Business Impact and Value Proposition
Ultimately, businesses invest in AI SaaS to achieve tangible benefits. Classifying products by their core value proposition helps to cut through the technical jargon and focus on what truly matters.
- Cost Reduction: Automating repetitive tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and minimizing errors can significantly lower operational costs.
- Increased Efficiency & Productivity: Streamlining workflows, accelerating decision-making, and freeing up employees from mundane tasks leads to higher overall productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalization, faster and more consistent support, and improved product discovery lead to happier and more loyal customers.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights, accurate predictions, and real-time analytics empower businesses to make smarter, more informed decisions.
- Risk Mitigation: Early detection of potential issues, enhanced cybersecurity, and proactive fraud prevention minimize business risks.
- Scalability: The ability of the solution to handle increasing data volumes and growing user demands without significant additional investment.
Practicalities: Integration and Technical Considerations

Even the most brilliant AI solution is only as good as its ability to fit into your existing ecosystem and operate reliably.
- Integration Capabilities: A key consideration is how easily the AI SaaS product integrates with your current business systems, such as CRM, ERP, or marketing automation platforms. Robust APIs and pre-built connectors are vital for seamless data flow.
- Data Handling and Infrastructure: AI thrives on data. An effective AI SaaS product must be capable of efficiently processing large and diverse data volumes, whether structured or unstructured. Understanding its reliance on specific cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and its ability to scale with your data growth is crucial.
- Adaptability and Evolution: The AI landscape is rapidly changing. A desirable AI SaaS solution should be designed to evolve, incorporating new features and adapting to changing data patterns and business requirements.
- Accuracy and Reliability: This is paramount. The AI’s outputs must be consistently accurate and reliable for businesses to trust and act upon its insights. This often involves understanding the model’s performance metrics and the provider’s commitment to continuous improvement.
- Ethical Considerations and Bias: As AI becomes more pervasive, ethical considerations are gaining prominence. It’s important to assess if the AI models are fair, unbiased, and comply with data privacy regulations (like GDPR). Transparency in how the AI makes decisions can also be a significant factor, especially in sensitive applications.
The Price Tag: Pricing and Packaging Models
Understanding the various pricing models is essential for budgeting and evaluating the long-term cost-effectiveness of an AI SaaS product.
- Usage-Based Pricing: Many AI SaaS products charge based on consumption – perhaps the number of API calls, data processed, or specific AI model usage. This can be cost-effective for variable workloads.
- Feature-Based Pricing: Different tiers might offer access to a basic set of AI features versus more advanced, premium functionalities.
- Per-Seat/User-Based Pricing: Similar to traditional SaaS, some AI products charge per user, which is common for collaborative tools.
- Hybrid Models: Often, providers will combine these approaches, offering a base subscription with additional charges for high usage or premium features.
- Value-Based Pricing: Increasingly, some AI SaaS providers are aligning their pricing with the direct business value or ROI delivered, though this can be harder to quantify.
By carefully considering these comprehensive classification criteria, businesses can move beyond the buzzwords and truly understand the capabilities and potential of AI SaaS products. This systematic approach allows for informed decision-making, ensuring that the chosen solutions are not just technologically advanced but also strategically aligned with organizational goals and poised to deliver real, measurable value.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About AI SaaS Product Classification
1. What is AI SaaS, in simple terms? AI SaaS (Artificial Intelligence Software as a Service) is software delivered over the internet, incorporating AI capabilities like machine learning or natural language processing, often on a subscription basis. It means you get powerful AI tools without needing to build or maintain them yourself.
2. Why is it important to classify AI SaaS products? Classifying AI SaaS products helps businesses understand their core functionality, identify how they can solve specific problems, compare different solutions effectively, and make informed purchasing decisions that align with their strategic goals.
3. What are the main types of AI technologies found in SaaS products? The main types include Machine Learning (ML) and Predictive Analytics, Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Conversational AI, Generative AI (like Large Language Models for text and code, or Vision Models for images), Computer Vision, and Deep Learning.
4. How does a company’s “use case” influence AI SaaS classification? A product’s use case dictates which business problem it aims to solve. For example, an AI SaaS product might be classified under “Customer Service” if its primary function is to automate customer inquiries, even if it uses NLP as its underlying technology.
5. What kind of business impact should I look for when classifying AI SaaS? Look for impacts like cost reduction, increased efficiency, enhanced customer experience, improved decision-making, reduced business risk, and the ability to scale operations more effectively.
6. What are the key technical considerations for AI SaaS solutions? Important technical considerations include how easily the product integrates with existing systems, its ability to handle large data volumes, its adaptability to future needs, its accuracy and reliability, and its adherence to data privacy and security standards.
7. How do AI SaaS pricing models typically work? Pricing models vary, but common approaches include usage-based (paying for what you use), feature-based (different pricing tiers for different functionalities), per-seat/user-based (paying per person), and hybrid models that combine these approaches. Some may also consider value-based pricing.
8. Is AI SaaS only for large enterprises? No, AI SaaS is designed to be accessible to businesses of all sizes. The cloud-based nature and subscription models make advanced AI capabilities available without requiring significant upfront investment in infrastructure or specialized AI teams.
9. What are the ethical considerations when adopting AI SaaS? Ethical considerations include ensuring the AI models are unbiased, transparent in their decision-making where necessary, and that they comply with all relevant data privacy regulations to protect sensitive information.
10. How can I ensure an AI SaaS product is reliable and accurate? To ensure reliability and accuracy, look for providers with proven track records, request case studies and customer testimonials, inquire about their model training processes, and consider starting with a trial or proof-of-concept to test the product in your specific environment.
Click for more amazing info. News MM

Tech
The Rise of AI-Powered Smartphones and Their Applications
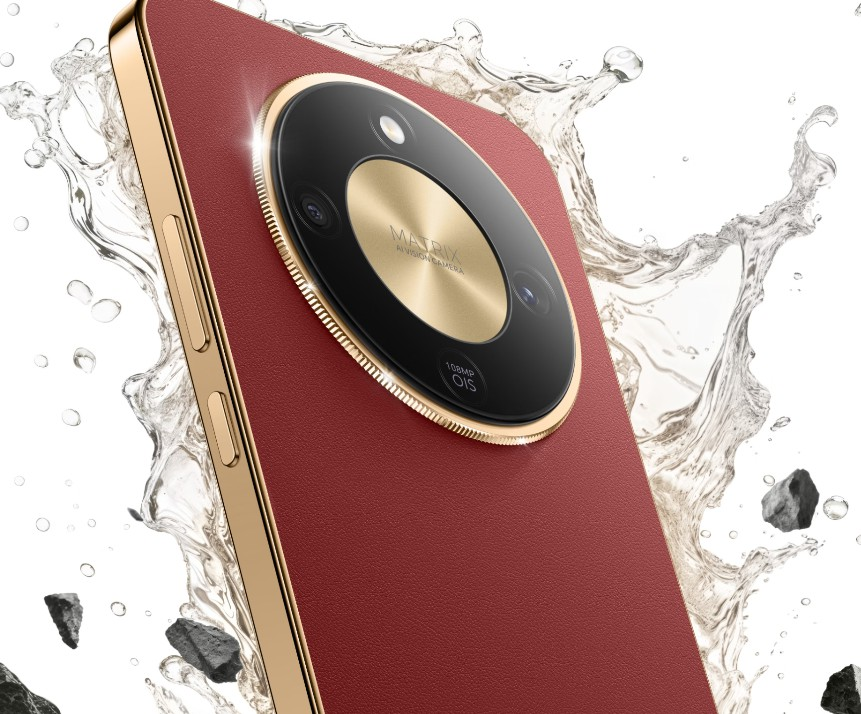

Smartphones have come a long way from basic communication tools. With AI integration,
devices now offer smarter functionalities that refine our experience. This shift signifies a major market evolution, improving user satisfaction by tailoring features to individual needs. Readers will explore the transformation driven by AI, focusing on how these advancements enhance everyday smartphone interactions. As AI continues to evolve, these devices become not just
tools for convenience but powerful companions that anticipate needs, learn habits, and redefine the very meaning of mobile intelligence.
Why Now? The Momentum Behind AI Smartphones
Advances in Mobile AI Chips & On-Device Processing
The rapid evolution of mobile AI chips enables complex tasks directly on devices. This advancement enhances speed and privacy by reducing reliance on cloud processing. On-device AI ensures efficient data handling, providing users with seamless and secure experiences. With every new generation of processors, smartphones gain the capability to handle machine learning
tasks instantly, supporting applications like advanced gaming, real-time translation, and personalized recommendations—all while consuming less energy and protecting user privacy.
Market Trends & Consumer Demand
Consumers increasingly demand smarter devices. AI-driven features like enhanced photography and voice recognition are now standard. The market rapidly adapts, with manufacturers prioritizing AI developments to meet these consumer expectations, driving the smartphone evolution. Companies are investing heavily in AI innovation to remain competitive, while
consumers benefit from more personalized, responsive experiences. From smart assistants to adaptive displays, these advancements ensure smartphones meet diverse global needs while setting new industry standards for innovation and usability.
Core AI Capabilities in Modern Smartphones
Intelligent Camera & Computational Photography
Smartphone cameras leverage AI to revolutionize photography. AI algorithms enhance image quality, adjusting settings in real-time to capture stunning photos effortlessly. Users enjoy
professional-grade results without needing advanced photography skills. Beyond aesthetics, AI-powered photography also improves facial recognition, scene detection, and low-light performance, ensuring every shot looks natural and detailed. This innovation transforms casual photography into an art form, empowering everyone to create visually compelling content with precision and ease directly from their smartphone.
Real-Time Translation and Voice Assistants
AI facilitates real-time translation, breaking language barriers instantly. Voice assistants powered by AI understand and perform complex tasks, offering users a hands-free, interactive experience. These capabilities redefine how we interact with our devices. As language models advance, users now enjoy smoother, more human-like conversations and accurate translations. From scheduling tasks to navigating foreign cities, AI-driven assistants simplify daily life, proving that
smartphones have become indispensable partners in both communication and productivity across cultures and languages.
Smart Resource, Battery & Performance Optimization
AI optimizes smartphone resources, intelligently managing battery life and performance. By learning user habits, AI ensures devices operate efficiently, extending battery life and improving overall functionality, adapting to each user’s unique usage patterns. This self-learning ability
allows smartphones to predict needs, close unused apps, and allocate resources dynamically. As a result, users experience faster, smoother performance with fewer interruptions, making devices not only smarter but also more sustainable and user-friendly for long-term productivity and entertainment.
Key Application Areas
Productivity & Personal Assistants
AI-driven personal assistants boost productivity by managing schedules, sending reminders, and automating tasks. These virtual helpers learn user preferences, providing a personalized
experience that simplifies daily routines. As they evolve, assistants integrate deeply with apps and smart devices, offering seamless multitasking and proactive suggestions. This allows users to save time, focus better, and achieve more—demonstrating how AI transforms smartphones into
indispensable personal organizers and productivity hubs for both work and life.
Security, Biometrics & Fraud Detection
AI enhances smartphone security with advanced biometric systems. These AI-enabled features
provide robust fraud detection, safeguarding user data and ensuring a secure digital environment. By learning behavioral patterns, AI can identify unusual activity instantly, preventing unauthorized access and fraud. From facial recognition to voice authentication, these innovations strengthen mobile security while maintaining user convenience. As cyber threats evolve, AI’s ability to adapt ensures that smartphones remain a trusted and resilient tool in protecting personal information.
Health, Wellness & Contextual Sensing
AI technology in smartphones supports health monitoring, tracking wellness metrics like heart rate and activity levels. Contextual sensing provides insights into user routines, promoting a healthier lifestyle by offering personalized health advice. With continuous learning, AI refines
these insights, identifying trends and suggesting proactive adjustments. Whether it’s encouraging hydration, reducing screen time, or improving sleep quality, smartphones now act as digital
wellness companions, guiding users toward balanced, data-driven health habits in everyday life.

Conclusion
AI smartphones mark a significant technological leap, enhancing our daily digital interactions.
Models like the HONOR Magic8 lite exemplify this progress by combining intelligent
performance with user-focused design. This transformation underlines the importance of staying informed about developments in mobile AI. Users and developers should remain alert, anticipating innovations that will redefine the smartphone landscape. As technology advances,
AI will continue to bridge the gap between human intuition and machine precision, making
devices more adaptive, secure, and essential than ever before. The future of mobile AI, reflected in phones such as the HONOR Magic8 Lite, promises seamless, personalized experiences for everyone, everywhere.
Tech
Why Mac Računala Are a Smart Choice for Everyday Use

Mac računala, also called Mac computers, are made by Apple. They are known for their quality, simple design, and easy use. Many people around the world use them for study, work, and personal needs. In this article, we will look at why Mac računala are a smart choice for everyday life. We will explore their history, design, features, benefits, and also the things you should know before buying one.
A Short History of Mac Računala
The first Mac was shown in 1984. It was different because it used a mouse and a clear screen with icons, not only text. This made it easy for people to use. Over time, Mac računala became more powerful and more beautiful in design. Apple moved from using Intel processors to its own chips called Apple silicon. These new chips made the computers faster and used less energy.
Modern Models of Mac Računala
Today, there are many types of Mac računala:
- MacBook Air: Light and thin, good for students and people who travel a lot.
- MacBook Pro: Stronger and better for heavy work like video editing.
- iMac: A desktop with a big screen, good for home and office.
- Mac mini: A small desktop that connects to any screen.
- Mac Studio: A powerful desktop for professionals.
- Mac Pro: The strongest Mac, used by people with very high demands.
Design and Build Quality
One reason people love Mac računala is the design. They are slim, light, and look modern. The body is made from strong aluminum, which makes them last a long time. The keyboards are comfortable, and the screens are sharp and bright. Apple pays attention to every small detail.

Hardware and Performance
Apple’s new Apple silicon chips, like the M1 and M2, make Mac računala very fast. They open apps quickly, run many tasks at the same time, and stay cool. The battery life is also strong. A MacBook Air, for example, can last more than 15 hours on one charge. This makes them very useful for daily work.
Software: macOS
All Mac računala use the macOS system. It is clean, simple, and safe. Many people like it because it does not crash often. It is also easy to connect with iPhone and iPad. For example, you can start writing an email on your phone and finish it on your Mac. Updates are free and keep the computer safe from problems.
Security and Privacy
Mac računala are known to be safer than many other computers. They have strong protection against viruses and other online risks. Apple also focuses on privacy. For example, Safari browser blocks trackers, and you can control which apps use your camera or microphone. This makes users feel more secure.
Easy Connection with Other Apple Devices
If you already have an iPhone, iPad, or Apple Watch, a Mac računar works even better. You can send files quickly with AirDrop, answer phone calls on your Mac, or unlock it with your Apple Watch. This kind of link between devices is one of Apple’s strongest points.
Everyday Benefits
For normal daily life, Mac računala give many benefits:
- Fast start and use: No waiting for the system to load.
- Long battery life: You can work or watch movies without worry.
- Good apps included: Photos, Pages, GarageBand, and iMovie come free.
- Good for students: Light and easy to carry.
- Good for work: Strong software for design, editing, and office work.
Challenges of Mac Računala
Even if Mac računala are very good, there are some things to keep in mind:
- Price: They cost more than many other computers.
- Upgrades: You cannot always change parts like memory or storage later.
- Software limits: Some special programs are not made for macOS.
- Games: Windows computers often have more support for gaming.
Should You Buy a Mac Računalo?
If you want a computer that is simple, safe, fast, and lasts for years, then a Mac računar is a smart choice. It is very good for students, creative workers, and people who already use other Apple devices. But if you want a low-cost computer or play many games, you may need to think more carefully.
Conclusion
Mac računala have a long history and a strong name in the computer world. They are built with care, run smoothly, and connect perfectly with other Apple devices. They may cost more, but many users say the experience is worth it. For everyday use, from writing emails to editing videos, Mac računala are a smart choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does Mac računar mean?
It is a Croatian word for Mac computer made by Apple.
2. Are Mac računala good for students?
Yes, they are light, strong, and have long battery life, which makes them great for study.
3. Can I play games on a Mac računar?
Yes, but Windows computers often have more game choices.
4. Do Mac računala get viruses?
They are safer than many computers, but it is still good to be careful online.
5. What is the difference between MacBook Air and MacBook Pro?
MacBook Air is light and thin, while MacBook Pro is stronger for heavy work.
6. Can I use Microsoft Office on a Mac računar?
Yes, Word, Excel, and PowerPoint work on Mac.
7. How long does a Mac računar last?
Many users keep them for 6–8 years or even longer with good care.
8. Are Mac računala easy to use?
Yes, macOS is simple and user-friendly, even for beginners.
9. Can I connect a Mac računar to an iPhone?
Yes, they work very well together and share files easily.
10. Is a Mac računar worth the price?
For many people, yes. It gives quality, speed, and a good user experience.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
Boost Organic Traffic with Garage2Global: Proven Strategies for 2025

In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, driving organic traffic is crucial for businesses looking to establish a strong online presence. As search engines get smarter and more competitive, leveraging effective strategies to boost organic traffic has become more essential than ever. One such strategy is partnering with Garage2Global, a renowned digital marketing agency that has proven expertise in helping businesses achieve long-term growth through organic search.
What is Organic Traffic and Why Does It Matter?

Before diving into the strategies, let’s first understand what organic traffic is and why it’s so important.
Organic traffic refers to visitors who land on your website through unpaid search results. These visitors come from search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo, without you having to pay for ads. This type of traffic is highly valuable because it is based on users actively searching for something related to your content, product, or service.
Why does it matter?
- Cost-Effective: Organic traffic reduces the need for expensive paid ads and provides a long-term, sustainable solution to drive website visitors.
- Higher Credibility: Websites that rank high in organic search results are often perceived as more trustworthy and credible by users.
- Long-Term Results: Unlike paid traffic, which stops once you stop paying, organic traffic continues to deliver results over time.
Given the importance of organic traffic, using reliable strategies is key to ensuring that your website ranks higher and attracts more visitors. Garage2Global has mastered this art and is helping businesses worldwide increase their organic reach.
Proven Strategies to Boost Organic Traffic with Garage2Global
Garage2Global specializes in a comprehensive approach to organic growth. Their strategies involve a combination of technical SEO, content marketing, ethical link-building practices, and on-page optimization. Below are some of the key strategies they employ to drive sustainable organic traffic.
1. In-Depth Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of any successful SEO strategy. Without understanding the words and phrases your target audience is searching for, it’s impossible to create content that resonates with them.
Garage2Global’s Approach:
- Target High-Impact Keywords: They focus on identifying not just high-volume keywords, but also long-tail keywords that are more specific and easier to rank for. These keywords tend to have lower competition and attract more qualified traffic.
- Analyze Search Intent: Garage2Global doesn’t just look at the keywords themselves. They analyze the intent behind those searches to ensure the content they create addresses user needs effectively.
Why it Works: Proper keyword research ensures that your content is tailored to what your audience is actively searching for. By ranking for relevant, high-quality keywords, you can significantly increase your organic traffic.
2. High-Quality, Engaging Content Creation
Once you have your keywords, the next step is creating content that’s not only optimized but also valuable to your audience. Content is what attracts visitors and keeps them engaged on your website.
Garage2Global’s Approach:

- Content That Answers Questions: They focus on creating content that provides real solutions to the problems your audience is facing. Whether it’s blog posts, guides, or infographics, Garage2Global ensures your content adds value.
- Regular Content Updates: Search engines like Google favor fresh, relevant content. Garage2Global helps you maintain a content calendar that regularly publishes new articles and updates old ones.
Why it Works: Google’s algorithm rewards websites that consistently produce high-quality content. By offering engaging and informative content, Garage2Global helps improve your website’s authority and relevance, leading to higher rankings and more organic traffic.
3. On-Page SEO Optimization
On-page SEO refers to the practices used on your website to help search engines understand the content and context of your pages. This includes optimizing elements like title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, and images.
Garage2Global’s Approach:
- Optimize for Featured Snippets: By formatting content to answer questions directly, Garage2Global helps businesses capture position zero in Google’s search results, often called the featured snippet.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: As more users browse the web on mobile devices, having a mobile-optimized website is essential for ranking. Garage2Global ensures your site’s design is responsive and user-friendly.
- Fast Loading Speed: Search engines prioritize fast-loading websites. Garage2Global ensures your site’s performance is optimized, helping you rank higher and keep visitors satisfied.
Why it Works: On-page SEO ensures that your website is optimized for both users and search engines. When done right, it helps improve visibility, drive traffic, and enhance the user experience.
4. Ethical Link Building
Link building remains one of the most effective strategies for boosting organic traffic. However, it’s essential to focus on ethical link-building strategies that comply with Google’s guidelines to avoid penalties.
Garage2Global’s Approach:
- Guest Posting: Garage2Global collaborates with reputable blogs and websites in your industry to place high-quality, relevant guest posts that include backlinks to your website.
- Influencer Collaborations: They work with influencers and thought leaders in your niche to build organic backlinks through social media mentions, interviews, and content collaborations.
Why it Works: High-quality backlinks from authoritative sources are one of Google’s top ranking factors. Ethical link-building practices help boost your website’s authority and trustworthiness, resulting in higher search engine rankings and more organic traffic.
5. Technical SEO
Technical SEO involves optimizing the technical aspects of your website to ensure that search engines can easily crawl, index, and rank your pages.
Garage2Global’s Approach:
- Improve Site Architecture: Garage2Global ensures your website has a clear and logical structure that search engines can easily navigate.
- Fix Crawl Errors: They identify and fix crawl errors that might prevent search engines from indexing your website properly.
- Implement Structured Data: Using structured data (schema markup) helps search engines better understand the content of your site and improves visibility in search results.
Why it Works: A technically sound website is easier for search engines to crawl, index, and rank. This results in better visibility, more traffic, and a smoother user experience.
6. Local SEO Optimization
If you have a local business, focusing on local SEO is essential for attracting organic traffic from nearby customers.
Garage2Global’s Approach:
- Google My Business Optimization: Garage2Global ensures your Google My Business profile is fully optimized, helping you show up in local searches and Google Maps.
- Local Citations: They help build consistent and accurate local citations (mentions of your business on other websites), which improves local search rankings.
Why it Works: Local SEO helps your business rank higher in location-based searches, which can drive more targeted traffic to your site and increase foot traffic to your physical store.
Conclusion
Boosting organic traffic is a critical element for businesses looking to grow their online presence and reach more potential customers. With the proven strategies employed by Garage2Global, you can enhance your SEO efforts and increase your visibility on search engines. From keyword research to technical SEO and ethical link building, each step plays a crucial role in achieving long-term, sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is organic traffic?
Organic traffic refers to visitors who come to your website through unpaid search engine results. This traffic is driven by your website’s SEO efforts. - How long does it take to see results from organic traffic?
Organic traffic growth can take time. Typically, it takes about 3 to 6 months to start seeing significant results from SEO efforts. - Why is organic traffic important?
Organic traffic is cost-effective, sustainable, and tends to bring more qualified leads compared to paid traffic. It also helps build long-term brand credibility. - What are long-tail keywords?
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific search phrases that usually have lower search volume but are easier to rank for and attract more targeted traffic. - How can I improve my website’s on-page SEO?
You can improve on-page SEO by optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, and content for relevant keywords, as well as ensuring your website is mobile-friendly and fast-loading. - What is link building, and why is it important?
Link building is the process of acquiring backlinks from other websites to your own. It’s important because high-quality backlinks signal to search engines that your website is authoritative and trustworthy. - What is the role of content in SEO?
Content plays a vital role in SEO because it helps search engines understand what your website is about. High-quality, engaging content also encourages visitors to stay on your site longer, which can improve rankings. - How do I measure organic traffic?
You can measure organic traffic using tools like Google Analytics, which track the number of visitors coming to your website from organic search results. - What is technical SEO?
Technical SEO involves optimizing the technical aspects of your website, such as its architecture, speed, and mobile responsiveness, to improve its visibility in search engines. - Can Garage2Global help my small business with SEO?
Yes, Garage2Global specializes in helping businesses of all sizes, including small businesses, improve their organic traffic and achieve sustainable growth through tailored SEO strategies.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
Antarvwsna: Unveiling Its Secrets for Personal Growth and Digital Wellness

Antarvwsna, a term derived from ancient Sanskrit, is becoming a focal point of discussions related to spirituality, mental well-being, and digital wellness. With roots deeply embedded in Indian philosophy, the concept of Antarvwsna extends beyond its traditional meaning and has made its way into modern practices, including technological innovations and digital wellness. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of Antarvwsna, its implications for personal growth, its connection to digital wellness, and how it is shaping modern wellness platforms.
What Is Antarvwsna?
A Spiritual and Philosophical Definition
The word Antarvwsna is a fusion of two Sanskrit words: antar meaning “inner” and vasana meaning “desire” or “impression.” Together, Antarvwsna refers to the deep-rooted inner desires, subconscious impressions, and unexpressed emotional longings that influence one’s behavior and decision-making.
In spiritual contexts, particularly in Advaita Vedanta, Antarvwsna is understood as the internal desires or impressions that shape a person’s journey and interactions with the world. These desires are thought to create cycles of karma, influencing an individual’s past, present, and future.
Psychological Interpretation
In modern psychology, Antarvwsna is often interpreted as repressed or suppressed desires. Psychologists believe that when desires or emotions are not fully acknowledged or dealt with, they can manifest in the form of stress, burnout, or anxiety. Addressing Antarvwsna involves recognizing and processing these subconscious desires, which can lead to better mental health and emotional well-being.
The Role of Antarvwsna in Personal Growth

Understanding Your Inner Desires
Personal growth begins with an understanding of who we are, including our inner desires and motivations. Antarvwsna helps us uncover these desires, many of which are hidden in the recesses of our subconscious. By exploring and acknowledging these desires, individuals can take conscious steps toward self-awareness, emotional balance, and personal development.
Through practices like meditation, journaling, and self-reflection, individuals can begin to uncover their Antarvwsna and understand how these desires are shaping their lives. This understanding is key to addressing unhealthy patterns and working toward a more fulfilling existence.
Connecting with Spirituality
Spiritual growth is also deeply linked to the exploration of Antarvwsna. In many traditions, addressing inner desires is seen as a way of purifying the mind and spirit. When one becomes aware of their deep-seated desires, it allows for the potential to let go of attachments that hinder spiritual progress.
By meditating on Antarvwsna, individuals can learn to align their desires with higher spiritual goals, such as compassion, peace, and mindfulness. As these inner desires are transformed, individuals can experience a deeper connection with themselves and the world around them.
Antarvwsna and Digital Wellness
The Intersection of Ancient Wisdom and Modern Technology
As technology continues to evolve, Antarvwsna has found a new relevance in the digital wellness space. The increasing use of digital platforms and AI has created an opportunity to merge ancient wisdom with modern technology to improve overall well-being.
One of the most significant developments is the rise of AI-driven wellness platforms that incorporate Antarvwsna principles. These platforms use AI to personalize meditation routines, mindfulness exercises, and mental health practices based on an individual’s emotional state and personal growth journey.
AI and Personal Growth

Some digital wellness platforms analyze data from wearable devices and mobile apps to track users’ emotional and physical states. These platforms then offer tailored guidance that addresses an individual’s unique needs, often incorporating practices to address Antarvwsna. By recognizing emotional patterns and desires, these platforms help individuals better understand their behavior and make conscious decisions to enhance their well-being.
Additionally, some apps now integrate Antarvwsna-focused content, such as mindfulness and breathwork exercises, to help individuals explore their desires in a safe, non-judgmental space. These digital tools empower users to align their personal growth goals with their subconscious desires, leading to enhanced emotional intelligence and healthier life choices.
The Future of Antarvwsna in Wellness
As Antarvwsna continues to be explored in both spiritual and technological contexts, its potential to revolutionize personal growth and digital wellness is enormous. With the rise of mindfulness apps, AI-driven wellness platforms, and mental health tech, Antarvwsna is becoming a central theme in the conversation about holistic well-being.
The future may see more sophisticated platforms that merge psychology, technology, and spirituality to guide individuals on a journey of personal transformation. These tools will likely harness advanced data analytics and AI to better understand human behavior and desires, helping individuals overcome inner conflict and achieve true wellness.
Conclusion
The concept of Antarvwsna is a powerful tool for personal growth and digital wellness. By understanding and addressing our inner desires, whether through ancient spiritual practices or modern digital tools, we can improve our emotional well-being, foster personal transformation, and live more fulfilling lives. As technology continues to evolve, the fusion of Antarvwsna with AI-driven wellness platforms offers an exciting future for individuals seeking a deeper connection with themselves and their personal growth journeys.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What does the term Antarvwsna mean?
Antarvwsna is derived from Sanskrit, combining “antar” (inner) and “vasana” (desire). It refers to the deep, subconscious desires that shape a person’s actions and experiences.
2. How does Antarvwsna relate to personal growth?
Understanding Antarvwsna allows individuals to uncover hidden desires, helping them become more self-aware and work through unhealthy patterns to achieve personal growth.
3. Can Antarvwsna help with mental health issues?
Yes, by recognizing and processing inner desires, individuals can address suppressed emotions that may be contributing to mental health issues like anxiety, stress, and depression.
4. How can I work with my Antarvwsna for personal development?
You can explore your Antarvwsna through practices such as meditation, journaling, and self-reflection. These techniques help bring awareness to your inner desires and guide you toward personal growth.
5. Is Antarvwsna connected to spiritual development?
Yes, in spiritual traditions, Antarvwsna is seen as a way to purify the mind and align one’s desires with higher spiritual goals, fostering deeper spiritual growth.
6. What role does technology play in addressing Antarvwsna?
AI-driven wellness platforms are incorporating Antarvwsna principles to provide personalized meditation, mindfulness, and mental health practices, making it easier for individuals to work through their subconscious desires.
7. Can digital wellness platforms help me understand my Antarvwsna?
Yes, many digital wellness platforms use AI to analyze your emotional and physical states, offering tailored guidance and exercises that help you explore and address your Antarvwsna.
8. Are there any apps that focus on Antarvwsna?
Yes, there are apps that incorporate Antarvwsna-focused content such as mindfulness practices, breathwork exercises, and mental health tips to help users explore their subconscious desires.
9. How can addressing Antarvwsna improve my well-being?
By acknowledging and processing your inner desires, you can reduce stress, gain emotional clarity, and create healthier life patterns, leading to better mental and emotional well-being.
10. What is the future of Antarvwsna in wellness?
As technology advances, the future of Antarvwsna in wellness may involve more sophisticated AI tools that blend psychology, technology, and spirituality to help individuals on their personal growth journeys.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
zryly.com internet: What It Is and Why You Should Care

In today’s digital age, having a reliable and efficient internet service is crucial. With a multitude of options available, it’s easy to overlook certain services that may not be as well-known as the big players. One such service is zryly.com, a rising name in the internet service sector. But what exactly is zryly.com internet, and why should you care about it?
What is Zryly.com Internet?
Zryly.com is a modern internet service provider (ISP) that offers a range of internet services to users worldwide. The company focuses on providing high-speed internet connections, reliable customer service, and competitive pricing for both individuals and businesses. Zryly.com prides itself on offering user-friendly packages and cutting-edge technology that cater to the growing demands of digital life.
Services Offered by Zryly.com
Zryly.com provides a wide variety of internet services, ensuring that they cater to both residential and commercial needs. Here’s a breakdown of the services they offer:
- Broadband Internet: Zryly.com offers high-speed broadband internet with a range of speeds to suit different user needs. This service is ideal for everything from browsing the web and streaming movies to handling large data uploads and downloads.
- Fiber-Optic Connections: For those who demand ultra-fast internet speeds and reliable connections, Zryly.com provides fiber-optic internet services. Fiber-optic technology is known for its superior speed and minimal downtime, making it perfect for households with multiple devices or businesses that rely on internet connectivity.
- Wireless Internet: Zryly.com also offers wireless internet options, providing flexibility for users who prefer not to be tethered to a wired connection. This can be ideal for mobile users or individuals who need an internet connection while on the go.
- Business Solutions: In addition to residential services, Zryly.com offers business-oriented solutions. This includes high-speed internet, customized plans for large organizations, and dedicated customer support to ensure smooth operations for businesses.
Features of Zryly.com Internet

What sets zryly.com internet apart from other internet providers? Here are some of its standout features:
1. High-Speed Connections
Zryly.com internet services offer some of the fastest speeds available in the market. Whether you’re streaming high-definition videos, playing online games, or working remotely, you can expect minimal lag and seamless browsing. Fiber-optic connections, in particular, offer speeds that can easily meet the demands of modern households and businesses.
2. Reliability
One of the biggest complaints users have about their internet services is connection reliability. Fortunately, Zryly.com has built its reputation around providing a reliable service with minimal interruptions. Their infrastructure is designed to handle a large number of users, and their customer support is responsive, ensuring that any potential issues are addressed quickly.
3. Affordable Plans
Zryly.com aims to make high-quality internet services available to all. The company offers competitive pricing on their internet packages, making it an affordable option for many users. They provide various plans based on speed and data needs, ensuring that there is something for everyone from casual users to heavy streamers and gamers.
4. Flexible Options
With different plans and connection types (such as broadband, fiber-optic, and wireless), Zryly.com allows users to choose the plan that best suits their needs. This flexibility is a major advantage for individuals, families, and businesses looking for internet solutions that match their specific requirements.
5. Excellent Customer Support
When it comes to internet providers, customer service can often be a hit or miss. However, Zryly.com stands out by offering excellent customer support. The company’s team is readily available to assist users with any issues or inquiries, ensuring a positive experience for all customers.
Why Should You Care About Zryly.com Internet?
1. Growing Popularity
As internet consumption continues to rise, more and more people are turning to alternative providers like Zryly.com for their internet needs. Whether you’re new to the service or considering switching from your current provider, it’s important to stay aware of the options available.
2. Affordable and Quality Service
Zryly.com makes high-speed internet more accessible with its affordable plans and reliable service. This can be particularly beneficial for those who are looking for great value without compromising on performance. If you’re tired of paying hefty bills for mediocre service, Zryly.com might be the solution you’ve been looking for.
3. Tailored Business Solutions
For businesses that rely on a stable and fast internet connection, Zryly.com offers tailored solutions. Their business packages are designed to ensure that businesses of all sizes have access to the necessary resources to thrive in today’s digital world.
4. Future-Proof Technology
With technology evolving rapidly, staying ahead of the curve is essential. Zryly.com uses fiber-optic technology, which is considered future-proof. By adopting such cutting-edge infrastructure, the company ensures that its customers will have access to fast and reliable internet for years to come.
How Does Zryly.com Compare to Other ISPs?
When comparing Zryly.com to other popular internet service providers, it stands out in a few key areas:
- Speed: Zryly.com’s fiber-optic connections are among the fastest available, providing faster download and upload speeds compared to traditional broadband connections.
- Reliability: Many users report fewer outages and interruptions with Zryly.com compared to other providers.
- Customer Service: Zryly.com’s customer service is widely praised for being responsive and helpful, which is a big selling point for users frustrated with other ISPs’ lackluster support.
- Affordability: With its competitive pricing, Zryly.com offers a more affordable solution without sacrificing quality, making it an attractive alternative to higher-priced ISPs.

Conclusion
Zryly.com internet is a rising star in the world of internet service providers, offering high-speed connections, reliability, and customer-focused solutions. Whether you’re a residential user or a business in need of fast and stable internet, Zryly.com has the tools and technology to meet your needs. With affordable pricing and exceptional customer service, it’s definitely a provider worth considering.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Zryly.com Internet
1. What is Zryly.com Internet?
Zryly.com is an internet service provider offering high-speed broadband, fiber-optic, and wireless internet options for both residential and business users.
2. Is Zryly.com internet available in my area?
Zryly.com is expanding rapidly, but availability depends on your location. You can check their website or contact their customer service to see if they provide service in your area.
3. What speeds does Zryly.com offer?
Zryly.com offers a range of speeds, with fiber-optic connections providing some of the fastest speeds available in the market.
4. Can I get internet service for my business from Zryly.com?
Yes, Zryly.com offers tailored business internet solutions with customizable plans to meet the needs of businesses.
5. How reliable is Zryly.com internet?
Zryly.com is known for its reliable internet connections, with minimal downtime and strong customer support to resolve any issues quickly.
6. Are Zryly.com’s prices competitive?
Yes, Zryly.com offers competitive pricing for its internet packages, making it an affordable option for many users.
7. What is fiber-optic internet, and why should I choose it?
Fiber-optic internet is a high-speed internet connection that uses light signals to transmit data. It is faster and more reliable than traditional broadband, making it a great choice for heavy internet users.
8. How can I sign up for Zryly.com internet?
You can visit Zryly.com’s website to sign up for their internet services. Alternatively, you can contact their customer service team for assistance.
9. Can I use Zryly.com’s internet for gaming?
Yes, Zryly.com’s high-speed internet is suitable for gaming, offering low latency and fast speeds to ensure a smooth experience.
10. What should I do if I have an issue with my Zryly.com internet service?
If you experience any issues, you can contact Zryly.com’s customer support team, which is known for being responsive and efficient in resolving problems.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
GetApkMarket: The Ultimate Guide to Downloading Safe APKs for Android Users

If you’re an Android user, you might have heard about third-party app stores like GetApkMarket. While Google Play is the go-to platform for most users, GetApkMarket provides an alternative for downloading apps that may not be available on the official platform. In this guide, we’ll explore what GetApkMarket is, how to use it, its pros and cons, and how to stay safe while downloading APKs from this source.
What is GetApkMarket?
GetApkMarket is a third-party Android app marketplace that offers a wide selection of APKs (Android Application Packages). Unlike Google Play, GetApkMarket allows users to download apps that may not be available on the official app store for various reasons. This includes apps that are region-restricted, modified versions of popular apps, or even apps that Google Play has removed for various reasons.
Key Features of GetApkMarket

- Wide Variety of Apps
GetApkMarket provides access to a vast collection of apps, including games, tools, and utilities. Many of these apps are either unavailable on Google Play or can only be downloaded through the official website. - Free Downloads
Most apps on GetApkMarket can be downloaded free of charge. While Google Play also has a free category, GetApkMarket offers more options without any hidden costs. - No Account Needed
Unlike Google Play, which requires a Google account for downloading apps, GetApkMarket allows users to download APKs without creating an account. - Modified APKs
GetApkMarket is particularly popular among users who are looking for modded versions of popular apps. These modified APKs often include premium features that are usually paid for, such as free in-app purchases or unlocked features.
How to Use GetApkMarket Safely
While GetApkMarket offers a convenient way to download Android apps, it’s essential to use caution. Downloading apps from third-party sources can expose your device to security risks, including malware, spyware, and other forms of malicious software. To ensure your safety, follow these steps:
Step 1: Enable Unknown Sources
Before you can install APKs from GetApkMarket, you’ll need to enable the “Install from Unknown Sources” option on your Android device. Here’s how to do it:
- Go to Settings on your Android device.
- Scroll down and select Security or Privacy.
- Toggle the switch to enable Install from Unknown Sources.
This step allows you to install apps that are not from the Google Play Store. Keep in mind that you should only enable this option when you trust the source of the APKs.
Step 2: Download the APK
Once you have enabled the “Unknown Sources” option, visit the GetApkMarket website and find the app you wish to download. Click on the download link for the APK file. Your device will begin downloading the file.
Step 3: Install the APK
After the download is complete, you can proceed with the installation process:
- Open the Downloads folder or tap on the notification that appears when the download finishes.
- Select the APK file.
- Tap Install to begin the installation process.
- Once the app is installed, you can open it from your home screen or app drawer.
Pros of Using GetApkMarket

- Access to Unavailable Apps
GetApkMarket provides access to apps that may not be available on the Google Play Store due to regional restrictions, policies, or other reasons. This opens up a wider variety of options for users who are looking for specific apps. - No Google Account Required
Unlike Google Play, which requires a Google account to download apps, GetApkMarket allows you to download apps directly without needing to sign in. - Free Modded Apps
Many users are attracted to GetApkMarket because it offers modded APKs, which come with unlocked premium features or no ads. This can be particularly appealing to users who want access to paid content for free. - Faster Updates
Some apps on GetApkMarket may receive updates faster than on Google Play, especially for apps that are not officially approved by Google. This can be beneficial if you’re looking for the latest features.
Cons of Using GetApkMarket
- Security Risks
One of the biggest downsides to downloading apps from third-party sources like GetApkMarket is the risk of installing malicious software. Since these APKs are not verified by Google, they could contain malware that can damage your device or steal your personal information. - Legal Issues
Downloading modded APKs or pirated versions of paid apps can lead to legal consequences. In some cases, these actions may violate copyright laws or the terms of service agreements of the app developers. - Device Stability Issues
Some APKs from GetApkMarket may not be optimized for your specific device, leading to crashes, lag, or other stability issues. This is especially true for modified or beta versions of apps. - Lack of Customer Support
Unlike official app stores like Google Play, GetApkMarket does not offer customer support. If you encounter issues with an app, you’re on your own when it comes to troubleshooting.
How to Stay Safe While Using GetApkMarket
To minimize the risks associated with using GetApkMarket, here are some safety tips:
- Use Antivirus Software
Install a reputable antivirus app on your Android device to scan APKs for malware before installing them. This will add an extra layer of protection against potentially harmful files. - Download from Trusted Sources
Always ensure that the website you’re downloading APKs from is trustworthy. Avoid downloading apps from sketchy websites or pop-up ads that may redirect you to unsafe locations. - Check App Permissions
Before installing any APK, review the permissions it requests. If an app asks for permissions that seem unnecessary for its function (e.g., a calculator app requesting access to your contacts), it’s best to avoid installing it. - Enable Google Play Protect
Google Play Protect is a built-in security feature that scans apps for malware and other potential risks. Ensure that this feature is enabled on your device for added protection.
Conclusion
GetApkMarket can be a valuable resource for Android users looking to access apps that aren’t available on Google Play, but it’s crucial to use it with caution. By following safety guidelines and ensuring that you download apps from trustworthy sources, you can enjoy a broader selection of apps while minimizing potential risks. Always weigh the benefits against the potential downsides before deciding to use third-party app stores like GetApkMarket.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is GetApkMarket?
GetApkMarket is a third-party Android app marketplace that offers APKs for apps that may not be available on the Google Play Store. It provides both free and modified versions of popular apps.
2. Is GetApkMarket safe to use?
While GetApkMarket provides access to a wide variety of apps, it also poses security risks. Apps downloaded from third-party sources may contain malware or other malicious software, so it’s important to exercise caution and use antivirus software.
3. How do I install apps from GetApkMarket?
To install apps from GetApkMarket, you must first enable “Install from Unknown Sources” in your device’s settings. Then, download the APK file from the website and follow the installation process.
4. Are the apps on GetApkMarket free?
Yes, most apps on GetApkMarket are free to download. However, some apps may offer premium features or modded versions that are usually paid for on Google Play.
5. Can I get modded apps on GetApkMarket?
Yes, GetApkMarket offers a variety of modded APKs, which may include premium features or removed ads, making them appealing to many users.
6. Can I trust GetApkMarket?
While GetApkMarket offers a vast selection of apps, there are risks involved, including the potential for downloading malicious software. It’s essential to use trusted antivirus software and download apps from reputable sources.
7. What are the dangers of downloading APKs from GetApkMarket?
The biggest risks include installing malware, violating copyright laws, and encountering stability issues with your device due to incompatible APKs.
8. How do I ensure the safety of my device when using GetApkMarket?
Use antivirus software, download APKs from trusted sources, and review app permissions before installing any APK.
9. Does GetApkMarket offer updates for apps?
Some apps on GetApkMarket may receive updates faster than on Google Play, especially for apps that are not officially approved by Google.
10. Is it illegal to use GetApkMarket?
Using GetApkMarket to download free apps is not illegal, but downloading modded or pirated versions of paid apps may violate copyright laws and the terms of service of the app developers.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
Exploring the Future of Technology: How GLDYQL is Shaping the Digital Landscape

In today’s rapidly evolving technological world, the buzz around digital frameworks and systems is ever-growing. One such term that’s gaining traction in both tech and digital circles is GLDYQL. While it might sound unfamiliar to many, it represents an emerging concept that could play a key role in how we interact with technology in the future. In this article, we’ll explore GLDYQL, its origins, applications, and how it’s shaping the digital landscape.
What is GLDYQL?
GLDYQL is a newly developed digital framework designed to optimize and streamline digital communication and decision-making processes using advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and quantum computing. The name itself is a blend of words, where each letter stands for a different technological concept:
- G: Global
- L: Logic
- D: Data
- Y: Yield
- Q: Quantum
- L: Language
Thus, GLDYQL stands for Global Logic Data Yield Quantum Language, which encapsulates its core focus on processing data in real time with quantum-level computing capabilities. But how does this work, and why is it so important? Let’s dive deeper.
How GLDYQL Works
At its core, GLDYQL combines multiple cutting-edge technologies to provide an integrated solution for real-time decision-making, efficient data processing, and communication across decentralized networks. The foundation of GLDYQL lies in quantum computing, which allows data to be processed in parallel at unprecedented speeds. Quantum computers can perform tasks much faster than traditional computers, making them a vital part of the GLDYQL framework.
The GLDYQL framework focuses on the following key elements:
1. Decentralized Data Networks
One of the unique features of GLDYQL is its ability to operate in decentralized networks. In contrast to traditional centralized systems, GLDYQL enables distributed computing where data processing and decision-making happen across multiple, independent nodes. This decentralization helps increase security, reduces the risk of system failures, and allows for faster data analysis.
2. AI-Driven Logic
Another crucial component of GLDYQL is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI systems within the framework are responsible for interpreting and analyzing large datasets, making logical decisions based on patterns and algorithms. By using AI, GLDYQL can ensure that the data flowing through its network is not only processed quickly but also interpreted intelligently.
3. Real-Time Data Yield
GLDYQL focuses on the concept of data yield the continuous flow of real-time, actionable data. This ensures that businesses, organizations, and individuals have access to the most up-to-date information at all times, enabling them to make informed decisions quickly.
4. Quantum Communication
Quantum communication is another critical feature of GLDYQL. With quantum cryptography and secure communication protocols, GLDYQL ensures that data is transmitted securely, even across vast and decentralized networks. Quantum communication uses the principles of quantum mechanics to protect data from interception and tampering, making it one of the most secure ways to transfer sensitive information.
Applications of GLDYQL
While GLDYQL is still a relatively new concept, its potential applications are vast. As industries and organizations continue to adopt more advanced technologies, GLDYQL could reshape how we interact with digital systems. Below are some areas where GLDYQL can make a significant impact.
1. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, GLDYQL could revolutionize data processing. With vast amounts of medical data generated every day, the ability to process and analyze this data quickly and accurately can lead to improved patient outcomes. For example, GLDYQL can help doctors and healthcare providers make faster diagnoses by analyzing patient data in real-time. Additionally, it could be used to manage medical records securely, ensuring patient privacy and compliance with data protection regulations.
2. Finance
Financial services could benefit significantly from the integration of GLDYQL. The financial sector deals with an immense amount of data, ranging from market trends to transaction records. By using quantum computing and AI to analyze this data, financial institutions can make better investment decisions, detect fraud more efficiently, and improve customer experiences. GLDYQL could enable real-time risk assessments and provide insights that would otherwise take longer to uncover.
3. Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is another area where GLDYQL can make a difference. In this industry, timely and accurate information is crucial for managing inventory, deliveries, and overall logistics. By implementing GLDYQL, supply chains can be optimized, ensuring that products reach consumers faster and more efficiently. Real-time data processing will allow businesses to react quickly to changing conditions, minimizing disruptions.
4. Smart Cities
As the world moves toward more connected and smart cities, GLDYQL could play a vital role. Smart cities rely on the seamless integration of data from sensors, devices, and infrastructure to manage resources like energy, water, and traffic. With GLDYQL, cities could analyze this data in real-time, improving public services, reducing energy consumption, and creating a more sustainable urban environment.
5. Education
In the field of education, GLDYQL could enable personalized learning experiences for students. By analyzing student data and preferences, GLDYQL could help create tailored educational content and learning paths. Teachers could receive real-time feedback on student progress, allowing them to adjust lessons and provide additional support where needed.
The Future of GLDYQL
As more industries explore the potential of GLDYQL, it’s clear that this technology will play a key role in the future of digital transformation. Quantum computing, AI, and decentralized networks are already changing the landscape of technology, and GLDYQL is at the intersection of these advancements. It has the potential to make digital systems faster, more secure, and more efficient.
In the next few years, we can expect GLDYQL to evolve and become a foundational component in various sectors. Its ability to handle vast amounts of data, process it quickly, and make intelligent decisions will unlock new opportunities and innovations. The future of GLDYQL looks promising, and as more businesses and industries begin to adopt it, the digital landscape will continue to evolve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GLDYQL is an exciting and innovative concept that could redefine how we process data and make decisions in the digital age. By integrating quantum computing, AI, and decentralized networks, GLDYQL promises to create more efficient, secure, and intelligent systems across various industries. As we move further into the future, this technology will likely play a central role in shaping the digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What does GLDYQL stand for?
- GLDYQL stands for Global Logic Data Yield Quantum Language, a framework combining AI, quantum computing, and decentralized systems for real-time data processing and decision-making.
- How does GLDYQL work?
- GLDYQL works by integrating quantum computing, AI-driven logic, decentralized data networks, and real-time data yield to enable faster, secure, and intelligent decision-making.
- What are the applications of GLDYQL?
- GLDYQL can be applied in various industries, including healthcare, finance, supply chain management, smart cities, and education.
- Why is GLDYQL important?
- GLDYQL is important because it allows for faster data processing, secure communication, and intelligent decision-making across decentralized networks.
- What is the role of quantum computing in GLDYQL?
- Quantum computing plays a central role in GLDYQL by enabling faster data processing through parallel computing, which traditional computers cannot match.
- Can GLDYQL help improve healthcare systems?
- Yes, GLDYQL can help by processing medical data in real-time, allowing healthcare providers to make faster diagnoses and improve patient care.
- How does GLDYQL impact the finance industry?
- In finance, GLDYQL can optimize data analysis for better investment decisions, fraud detection, and customer experience improvements.
- How secure is GLDYQL?
- GLDYQL is highly secure due to its use of quantum cryptography, which ensures that data is transmitted safely, even in decentralized networks.
- Is GLDYQL already in use?
- While still a developing concept, GLDYQL is gaining attention and could become more widespread as quantum computing and decentralized systems evolve.
- What is the future of GLDYQL?
- The future of GLDYQL looks bright, with continued advancements in quantum computing and AI likely making it a foundational technology for industries across the globe.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
Unveiling Ghuk-Y44551/300: The Future of Smart Automation is Here
In our rapidly evolving world, technology is constantly pushing boundaries, offering innovative solutions that reshape how we live and work. Among the latest advancements making waves is the Ghuk-Y44551/300, a cutting-edge smart device poised to redefine automation across various sectors. This article will delve into the details of the Ghuk-Y44551/300, exploring its features, potential applications, and the benefits it brings to the table. We’ll aim to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of this exciting piece of technology, making it accessible to everyone.
What Exactly is the Ghuk-Y44551/300?
At its core, the Ghuk-Y44551/300 is a sophisticated smart automation unit. Think of it as a central brain designed to manage and optimize various systems, from simple household tasks to complex industrial processes. It’s built with a focus on performance, reliability, and seamless integration, making advanced technology accessible and user-friendly.
Imagine a device that can intelligently control your home’s lighting based on your presence, optimize the energy consumption of a factory, or meticulously monitor environmental conditions in an agricultural setting – that’s the kind of power the Ghuk-Y44551/300 aims to deliver. It’s more than just a gadget; it’s an intelligent system designed to enhance efficiency and streamline operations.
Key Features That Set It Apart

The Ghuk-Y44551/300 boasts a range of impressive features that contribute to its versatility and effectiveness:
- High-Speed Data Processing: Equipped with a powerful processor, this device can handle and analyze large amounts of data in real-time. This capability is crucial for tasks requiring quick decision-making and efficient operation, such as in industrial automation or complex smart home scenarios.
- Intelligent Automation Capabilities: The core strength of the Ghuk-Y44551/300 lies in its ability to automate tasks intelligently. It can be programmed to respond to specific conditions, learn from data patterns, and adjust operations accordingly. For instance, in a manufacturing plant, it could monitor machine performance and automatically make adjustments to optimize output and prevent breakdowns.
- Robust Security Framework: In today’s interconnected world, security is paramount. The Ghuk-Y44551/300 incorporates advanced cybersecurity measures, including firewalls and data encryption, to protect sensitive information and ensure secure operation. This is particularly important when the device is integrated into larger networks or controls critical systems.
- Seamless Integration and Connectivity: The Ghuk-Y44551/300 is designed to work harmoniously with other smart devices and systems. It offers various connectivity options, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Ethernet, allowing for easy integration into existing infrastructure. This flexibility makes it a versatile solution for diverse applications.
- Energy Efficiency: Recognizing the importance of sustainability, the Ghuk-Y44551/300 is engineered for optimal energy efficiency. This not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes its environmental impact, making it a responsible choice for both businesses and individuals.
- Durable and Reliable Design: Built to withstand various operating conditions, the Ghuk-Y44551/300 features a robust and reliable design. This durability ensures consistent performance even in demanding environments, contributing to its long-term value and dependability.
- User-Friendly Interface: Despite its advanced capabilities, the Ghuk-Y44551/300 is designed with user convenience in mind. Its intuitive interface and straightforward setup process make it accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Over-the-Air Updates: To ensure it remains up-to-date with the latest features and security patches, the Ghuk-Y44551/300 supports over-the-air software updates. This eliminates the need for manual updates and ensures that the device is always performing at its best.
Potential Applications Across Different Sectors

The versatility of the Ghuk-Y44551/300 opens up a wide range of potential applications across various industries and everyday life:
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing and production, it can be used to monitor and control machinery, optimize production lines, manage inventory, and ensure quality control. Its high-speed processing and intelligent automation capabilities can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and output.
- Smart Homes: For homeowners, the Ghuk-Y44551/300 can serve as a central hub for managing smart home devices. It can automate lighting, climate control, security systems, and entertainment, creating a more comfortable, convenient, and energy-efficient living environment.
- Agriculture: In the agricultural sector, it can be used for precision farming. This includes monitoring soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, as well as automating irrigation and fertilization systems. This can lead to increased yields and more sustainable farming practices.
- Healthcare: The device can play a role in remote patient monitoring, managing medical equipment, and streamlining hospital operations. Its data processing and security features make it suitable for handling sensitive healthcare information.
- Energy Management: The Ghuk-Y44551/300 can be used to optimize energy consumption in buildings and industrial facilities. By monitoring energy usage patterns and automatically adjusting systems, it can help reduce costs and promote energy conservation.
- Environmental Monitoring: Its sensor integration capabilities allow it to be used for monitoring environmental conditions such as air and water quality. This data can be crucial for research, conservation efforts, and public health initiatives.
Benefits of Implementing the Ghuk-Y44551/300
The adoption of the Ghuk-Y44551/300 offers numerous benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: By automating tasks and optimizing processes, the device helps organizations and individuals achieve greater efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Costs: Energy optimization, minimized manual intervention, and predictive maintenance capabilities can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
- Improved Reliability: The robust design and advanced monitoring features ensure consistent and reliable operation, minimizing downtime and potential disruptions.
- Enhanced Security: The built-in security measures protect against cyber threats and ensure the integrity of data and operations.
- Data-Driven Insights: The device’s ability to collect and analyze data provides valuable insights that can inform decision-making and lead to continuous improvement.
- Greater Convenience: For personal use, it offers enhanced convenience and control over various aspects of daily life.
- Sustainability: Its energy-efficient design contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and waste.
The Future with Ghuk-Y44551/300
The Ghuk-Y44551/300 represents a significant step forward in the realm of smart automation. Its combination of advanced features, versatility, and user-friendly design positions it as a key technology for the future. As we continue to embrace interconnected devices and intelligent systems, innovations like the Ghuk-Y44551/300 will play an increasingly vital role in shaping a more efficient, convenient, and sustainable world. Whether in industrial settings, our homes, or various other sectors, the potential of the Ghuk-Y44551/300 to drive positive change is immense, promising a future where technology seamlessly enhances our lives and work.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the primary function of the Ghuk-Y44551/300? The primary function is to provide intelligent automation and control for various systems, enhancing efficiency and streamlining operations across different sectors and in smart homes.
- Is the Ghuk-Y44551/300 difficult to set up and use? No, it’s designed with a user-friendly interface and a straightforward setup process, making it accessible even for those with limited technical knowledge.
- What kind of security measures does it have? It incorporates robust security features, including firewalls and data encryption, to protect against cyber threats and ensure secure operation.
- Can it integrate with my existing smart home devices? Yes, the Ghuk-Y44551/300 is designed for seamless integration with a wide range of smart devices and systems through various connectivity options like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
- How does it contribute to energy saving? It is engineered for energy efficiency and can optimize the energy consumption of connected systems, leading to reduced energy bills and a lower environmental impact.
- In what industries can the Ghuk-Y44551/300 be used? It has potential applications in various industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, energy management, and environmental monitoring, as well as in smart homes.
- Does the device receive software updates? Yes, it supports over-the-air (OTA) software updates, ensuring that it always has the latest features, improvements, and security patches.
- Is the Ghuk-Y44551/300 durable enough for industrial use? Yes, it is built with a robust and reliable design to withstand various operating conditions, making it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
- Where can I find more detailed technical specifications? Detailed technical specifications can typically be found in the product’s official documentation or on the manufacturer’s website.
- What are the main benefits of using the Ghuk-Y44551/300 compared to traditional automation systems? Key benefits include intelligent automation capabilities, high-speed data processing, robust security, seamless integration, user-friendliness, and energy efficiency, often surpassing the capabilities of traditional systems.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
What Is UVLACK? Understanding the Benefits of UV Coatings

In today’s world, advancements in technology continue to shape industries in innovative ways. One such advancement is the use of UV coatings, specifically UVLACK. This remarkable material has made its way into several fields, from manufacturing to automotive and even the furniture industry. But what exactly is UVLACK, and how does it benefit various industries?
What Is UVLACK?
UVLACK refers to a type of coating or varnish that is cured using ultraviolet (UV) light. This process is often called UV curing, where the coating undergoes a chemical reaction when exposed to UV light, making it dry instantly. Unlike traditional coatings that require air drying or heat, UVLACK does not need prolonged exposure to heat or oxygen. Instead, it relies on UV light to solidify and bond with the substrate, making it an efficient and fast-curing solution.
UVLACK coatings are primarily used to create a high-gloss finish on surfaces, making them ideal for applications where durability, aesthetics, and efficiency are important. Commonly found in industries such as automotive, electronics, and furniture, UVLACK has gained popularity due to its many advantages over conventional coatings.
How Does UVLACK Work?

The process of UV curing is relatively straightforward. When a surface is coated with UVLACK, it is exposed to UV light. This exposure causes the liquid coating to undergo a polymerization process, where the molecules bond together, creating a hardened, durable finish. The UV light acts as a catalyst, triggering the chemical reaction that leads to the rapid hardening of the coating.
One of the significant advantages of UV curing is speed. Unlike traditional methods, where coatings may take hours or even days to cure, UVLACK coatings can be fully cured in a matter of seconds or minutes under UV light. This drastically reduces production time, making it highly efficient for large-scale manufacturing processes.
Benefits of UVLACK Coatings
1. Quick Curing Time
One of the standout features of UVLACK is its quick curing time. Unlike traditional coatings, which rely on air drying or baking, UVLACK hardens instantly when exposed to UV light. This eliminates long waiting times and helps businesses streamline their production processes.
2. Durability
UVLACK coatings are known for their excellent durability. Once cured, the coating becomes highly resistant to scratches, abrasions, and chemical damage. This makes UVLACK an excellent choice for products that need to withstand frequent handling or exposure to harsh conditions.
3. Environmental Benefits
UVLACK is an environmentally friendly option for many industries. Traditional coatings often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can be harmful to the environment. UVLACK, on the other hand, contains little to no VOCs, making it a safer and greener choice for manufacturers.
4. High Gloss Finish
The curing process of UVLACK produces a smooth, high-gloss finish that enhances the visual appeal of the product. Whether used on automotive parts, furniture, or electronics, the shiny finish provided by UVLACK can elevate the overall aesthetic of the product.
5. Energy Efficiency
The UV curing process is more energy-efficient compared to traditional heat-based curing methods. Since UV light is a targeted energy source and does not require the heating of large ovens, businesses can save on energy costs.
6. Chemical Resistance
UVLACK coatings are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including oils, solvents, and cleaners. This makes it an ideal choice for products that will be exposed to harsh chemicals or frequent cleaning.
7. Enhanced Adhesion
UVLACK coatings provide excellent adhesion to various substrates, including metals, plastics, and wood. This ensures that the coating remains firmly in place and does not peel or chip off easily over time.
8. Reduced Waste
The UV curing process is highly efficient and produces less waste compared to traditional methods. The liquid UVLACK coating hardens quickly and does not require additional layers or excess material, resulting in reduced waste and a more efficient use of resources.
9. Non-Toxic
Since UVLACK coatings have little to no VOCs, they are considered safer for workers and consumers. The absence of toxic fumes makes UVLACK a safer option in industries that prioritize workplace health and safety.
10. Customizable for Different Applications

UVLACK coatings can be formulated for various applications. Whether you need a matte, glossy, or textured finish, UVLACK can be customized to suit the specific requirements of your product, making it a versatile solution across different industries.
Applications of UVLACK Coatings
1. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, UVLACK coatings are often used for exterior parts like bumpers, dashboards, and trim pieces. The quick drying time and durability of UVLACK make it an ideal choice for automotive manufacturers who need high-performance coatings that can withstand exposure to the elements.
2. Electronics
UVLACK is commonly used to coat electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. The high-gloss finish not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of these products but also provides added protection against scratches and wear.
3. Furniture and Woodworking
Furniture manufacturers use UVLACK coatings to create sleek, durable finishes on wood products. The smooth, glossy finish gives furniture a high-end look, while the scratch resistance ensures the product stays looking new for longer.
4. Packaging
UVLACK is also used in the packaging industry, particularly for items like labels and bottles. The ability to quickly cure the coating makes it perfect for mass production in packaging, where high volumes need to be processed quickly.
5. Print Industry
In the printing industry, UVLACK is applied to printed materials to enhance the visual quality and durability of the print. It ensures that the print remains sharp, vibrant, and resistant to fading.
Conclusion
UVLACK is a groundbreaking technology that offers numerous benefits across various industries. Its quick curing time, durability, and environmental friendliness make it an excellent choice for manufacturers looking to enhance their products. Whether you are in the automotive, electronics, or furniture industry, UVLACK coatings provide the perfect combination of performance and aesthetics.
10 Frequently Asked Questions About UVLACK
- What is UVLACK used for?
- UVLACK is used in various industries such as automotive, electronics, furniture, packaging, and printing. It provides a durable, high-gloss finish to products and enhances their overall durability.
- Is UVLACK safe to use?
- Yes, UVLACK is considered safe to use as it contains little to no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a non-toxic and environmentally friendly option.
- How long does it take for UVLACK to cure?
- UVLACK coatings cure almost instantly when exposed to UV light, typically within a few seconds to a minute, depending on the thickness of the coating.
- Can UVLACK be used on all materials?
- UVLACK can be applied to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, providing excellent adhesion to these substrates.
- Is UVLACK resistant to chemicals?
- Yes, UVLACK coatings offer excellent resistance to various chemicals, including solvents, oils, and cleaners, making them ideal for products exposed to harsh environments.
- How is UVLACK different from traditional coatings?
- Unlike traditional coatings, UVLACK cures through UV light rather than heat or air drying. This results in faster curing times and a more durable finish.
- Is UVLACK environmentally friendly?
- Yes, UVLACK coatings are environmentally friendly as they produce little to no VOCs, which are harmful to both human health and the environment.
- Can UVLACK coatings be customized?
- Yes, UVLACK coatings can be customized to achieve various finishes, such as glossy, matte, or textured, depending on the application.
- How does UVLACK help in reducing production costs?
- UVLACK’s fast curing time helps reduce production costs by eliminating the need for long drying times and reducing energy consumption.
- Is UVLACK more expensive than traditional coatings?
- While UVLACK coatings may be initially more expensive, they offer long-term cost savings due to their fast curing times, durability, and energy efficiency.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
Tech
ATFBORU: Your Guide to Reddit Story Endings

Have you ever found yourself utterly engrossed in a captivating story on Reddit, following every twist and turn, only to be left hanging? You refresh the page daily, hoping for an update, a resolution, anything that provides closure to the saga. If this sounds familiar, then you’re about to discover a game-changer: ATFBORU.
For many avid Reddit readers, the quest for “what happened next?” is a persistent one. So many compelling narratives unfold in subreddits like r/AITA, r/TIFU, r/Relationship_Advice, and r/ProRevenge, drawing us in with their raw honesty, unexpected turns, and often, profound insights into human nature. But the internet is vast, and tracking down those elusive updates from original posters (OPs) can feel like searching for a needle in a digital haystack. This is precisely where ATFBORU steps in, offering a much-needed beacon for resolution seekers.
What Exactly is ATFBORU? The Reddit Story Resolution Hub

At its core, ATFBORU serves as a dedicated platform for curating and presenting the highly anticipated updates and conclusions to popular Reddit stories. Think of it as your personal librarian for internet sagas, meticulously tracking threads and delivering the crucial “rest of the story” that so many of us crave. The name itself, while not officially confirmed by the platform, is often speculated to stand for “Am I the Fool? Best of Reddit Updates” – a nod to the prominent subreddit r/AITA, which is a frequent source of its content.
The primary goal of ATFBORU is to provide closure. Reddit, by its very nature, is a dynamic and often fragmented platform. A user might post a deeply personal dilemma, receive thousands of comments and advice, and then… silence. Days, weeks, or even months can pass before an OP provides an update, if they ever do. ATFBORU bridges this gap, acting as a centralized repository for these crucial follow-ups, ensuring that readers can experience the full narrative arc, from the initial post to its eventual resolution.
Why is ATFBORU Such a Game-Changer for Reddit Enthusiasts?
Before ATFBORU, finding updates to captivating Reddit stories was often a haphazard and frustrating process. You might save a post, set a reminder, or simply hope to stumble upon the update organically. This manual tracking was inefficient and often led to missed conclusions. ATFBORU addresses these pain points directly:
- Convenience and Efficiency: Instead of endlessly scrolling or searching, ATFBORU compiles all known updates in one accessible location. This saves immense time and effort for readers.
- Guaranteed Closure: The platform is dedicated to seeking out and presenting resolutions, giving readers the satisfaction of knowing “how it all ended.” This is particularly valuable for stories that evoke strong emotional responses or spark widespread debate.
- Curated Quality: ATFBORU doesn’t just repost everything. It often involves a degree of curation, focusing on significant updates that genuinely move the story forward, rather than minor edits or tangential comments. This ensures that the updates provided are impactful and meaningful.
- Discoverability: Sometimes, a story’s initial post might have been popular, but its update might not have garnered as much attention. ATFBORU helps these updates find their audience, ensuring that the full narrative gets the recognition it deserves.
- Community Satisfaction: For many, engaging with Reddit stories is a form of communal storytelling. ATFBORU enhances this experience by allowing the community to collectively witness the conclusion of these shared narratives.
The Inner Workings: How Does ATFBORU Gather Its Information?

While the exact proprietary methods of ATFBORU remain somewhat behind the curtain, its operations likely involve a combination of sophisticated tracking and community engagement:
- Automated Monitoring: It’s highly probable that ATFBORU employs automated systems and algorithms to monitor popular subreddits known for long-form stories. These systems would identify posts that generate significant engagement, comments, and ongoing discussion, flagging them as potential candidates for future updates.
- Keyword and User Tracking: The platform might track specific keywords (e.g., “update,” “follow-up,” “edit”) within posts and comments. Furthermore, it could monitor the posting history of original posters (OPs) for threads that have gone viral, looking for subsequent posts from the same user that might serve as an update.
- Community Submissions and Tips: A crucial element of many content aggregation platforms is user contribution. It’s plausible that ATFBORU benefits from a community of avid Reddit readers who submit links to updates they discover. This crowdsourcing method significantly expands the platform’s reach and ability to find elusive follow-ups.
- Manual Verification and Curation: To maintain quality, a degree of manual review is likely involved. This ensures that the “updates” are genuine, relevant, and not simply spam or unrelated content. Curators would assess the significance of each update, ensuring it truly provides the anticipated resolution.
- Archiving and Categorization: Once an update is identified and verified, it would be linked to its original story and perhaps categorized by subreddit, theme, or impact. This makes the vast library of stories easily navigable for users.
The Spectrum of Stories: What Kind of Content Can You Expect?
ATFBORU primarily focuses on stories that have a clear beginning, middle, and potential end. This includes a wide array of narratives from popular advice-driven and confessional subreddits:
- r/AITA (Am I the Asshole?): These are perhaps the most common, where users present a conflict and ask the community to judge who was in the wrong. Updates often reveal the fallout of the conflict, reconciliation efforts, or the OP’s personal growth.
- r/Relationship_Advice: Stories here often involve complex interpersonal dynamics, family disputes, or romantic challenges. Updates can detail breakups, make-ups, or significant life changes resulting from the advice given.
- r/TIFU (Today I Fucked Up): These are tales of comedic or disastrous blunders. Updates might explain the long-term consequences of the “fuck up,” how the OP recovered, or newfound wisdom.
- r/ProRevenge & r/MaliciousCompliance: Stories of justified retaliation or clever adherence to rules. Updates often reveal the satisfaction of seeing justice served or the unintended consequences for those who deserved it.
- r/TrueOffMyChest & r/Confession: Deeply personal revelations. While not always seeking advice, these posts often leave readers wondering about the aftermath. Updates can provide insights into the emotional journey of the OP.
- Other Niche Subreddits: Depending on the popularity and update frequency of stories, ATFBORU might also feature content from subreddits like r/AmItheCloaca (for pet-related AITA stories), r/pettyrevenge, and various professional or life-experience based communities.
The common thread is the human element – real people sharing real experiences, and the desire of readers to see how those experiences evolve.
Beyond the Updates: The Broader Impact of ATFBORU
ATFBORU’s existence highlights several interesting aspects of our digital consumption habits and the nature of online communities:
- The Desire for Narrative Completion: Humans are wired for storytelling, and we naturally seek closure. In an age of infinite content streams, platforms like ATFBORU satisfy this fundamental psychological need.
- The Power of Community-Driven Content: Reddit thrives on user-generated content, and ATFBORU leverages this by recognizing the collective investment readers make in these stories. It’s a testament to how online communities can organically create compelling narratives.
- A Solution to Information Overload: In a sea of daily posts, finding specific updates can be overwhelming. ATFBORU acts as a filter, presenting only the most relevant and sought-after information, simplifying content consumption.
- Preserving Digital Lore: Many of these Reddit stories become internet lore, discussed and referenced years later. By compiling the full narrative, ATFBORU inadvertently helps to preserve these digital artifacts, making them accessible for future generations of internet users.
- Bridging the Gap Between Creator and Audience: While Reddit provides the initial platform, ATFBORU helps ensure that the OP’s follow-up efforts reach their intended and invested audience, fostering a stronger connection between storytellers and their readers.
Navigating ATFBORU: Tips for Readers
If you’re ready to dive into the world of Reddit story endings, here are a few tips to enhance your experience with ATFBORU (or similar platforms that provide curated updates):
- Start with What You Know: If there’s a specific Reddit story you’ve been following, use the platform’s search function to see if an update is available.
- Browse Popular Categories: Explore sections dedicated to subreddits like r/AITA or r/Relationship_Advice to find updates for stories you might have missed or forgotten about.
- Check for “New Updates” Sections: Many platforms will highlight recently added or discovered updates, making it easy to stay current.
- Engage Responsibly: Remember that these are often real people sharing real-life dilemmas. While reading the updates, maintain a respectful and empathetic perspective.
- Consider Subscribing (if applicable): If the platform offers a newsletter or notification service, subscribing can ensure you never miss out on new resolutions.
The Future of Digital Storytelling and Resolution
As digital content continues to evolve, the demand for curated, resolved narratives will likely grow. ATFBORU, or platforms like it, represent a valuable service in the vast and often chaotic landscape of the internet. They transform fragmented posts into complete stories, satisfying our innate human desire for closure and making the rich tapestry of Reddit’s user-generated content even more rewarding to explore.
So, the next time you finish a captivating Reddit post and wonder, “But what happened next?”, remember that there’s a good chance ATFBORU has the answer you’re looking for, ready to deliver that satisfying conclusion.
Frequently Asked Questions About ATFBORU
1. What does ATFBORU stand for? While not officially confirmed by the platform, it is widely speculated to stand for “Am I the Fool? Best of Reddit Updates,” a nod to the popular subreddit r/AITA.
2. Is ATFBORU an official Reddit platform? No, ATFBORU is an independent platform that curates content from Reddit. It is not affiliated with or endorsed by Reddit Inc.
3. How does ATFBORU find Reddit story updates? ATFBORU likely uses a combination of automated monitoring, keyword tracking, and potentially community submissions to identify and gather updates from original posters (OPs) across various subreddits.
4. What kind of Reddit stories does ATFBORU focus on? It primarily focuses on stories that have a clear narrative arc and potential for follow-up, commonly from subreddits like r/AITA, r/Relationship_Advice, r/TIFU, r/ProRevenge, and other advice or confessional-based communities.
5. Is ATFBORU free to use? Generally, platforms like ATFBORU that aggregate publicly available Reddit content are free for users to access and read.
6. Can I submit an update to ATFBORU if I find one? Some aggregation platforms offer a way for users to submit links to updates they’ve discovered. You would need to check the specific ATFBORU platform for this feature.
7. How often is ATFBORU updated with new content? The frequency of updates depends on the platform’s operations and the availability of new Reddit story updates. Reputable platforms strive to be updated regularly to provide timely conclusions.
8. Is the information on ATFBORU always accurate? ATFBORU aims to provide accurate updates, but like any content aggregated from user-generated sources, it’s always good to approach with a critical eye. The platform’s curation process helps ensure reliability.
9. Can I find older Reddit story updates on ATFBORU? Yes, one of the benefits of ATFBORU is its archiving capability. You can often find resolutions to older, well-known Reddit stories alongside newer ones.
10. Why is closure for Reddit stories so important to readers? Humans have a natural desire for narrative completion and closure. When we invest emotionally in a story, whether fictional or real, we want to know “how it ends.” ATFBORU satisfies this fundamental psychological need, turning fragmented posts into complete and satisfying narratives.
Click for more amazing info. News MM
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoIndia Rose Brittenham: All You Need to Know About Heather Thomas’ Daughter
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoMargot Rooker: All You Need to Know About Michael Rooker’s Wife
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoRobert Noah? All You Need to Know About Trevor Noah’s Father
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoNadia Farmiga? All You Need to Know About Taissa Farmiga’s Sister
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoJackie Witte? All You Need to Know About Paul Newman’s First Wife
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoCheryl Pistono? All You Need to Know About Kareem Abdul-Jabbar’s Ex-Girlfriend
-

 Celebrity9 months ago
Celebrity9 months agoWho is the Father of Jay-Z? Biography of Adnis Reeves
-

 Celebrity10 months ago
Celebrity10 months agoAbigail S. Koppel? All You Need to Know About Leslie Wexner’s Wife












